Explain Conservation of Angular Momentum
When a body rotates (spins like a top) or revolves (moves in a circle around a central point), all of the rules that we have used to calculate linear motion and motion in 2-dimensions can be rewritten as rotational equivalents to calculate motion of rotation and revolution. Where in Newton's Laws we used force, F, now we talk about torque, ζ, and distance, d, becomes angle, θ, speed, v, becomes angular speed, ω, and acceleration, a, becomes angular acceleration, α. Mass becomes rotational inertia, I, a measure of how easy or hard it is to get a body rotating. We can define an angular momentum, L
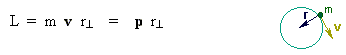
which must be conserved if there is no net applied torque on the body, just as momentum must be conserved if there are no net forces on a body. If the body is in rotational equilibrium, no net torque, it can undergo no net angular acceleration. Torque is a force applied to spin or rotate a body and is calculated as the force perpendicular to the radius times the radius to the center of rotation
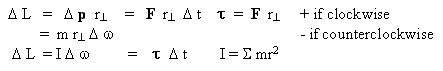
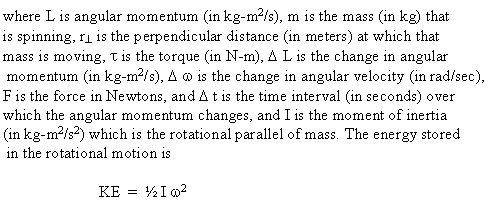
Table of Moments of Inertia, I, for Various Spinning shapes:
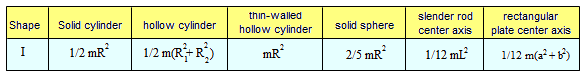
This tells us that for the same size R, a thin-wall hollow cylinder takes more torque to start rotating than a solid cylinder of the same mass and radius. A solid sphere of the same mass and radius would require even less torque to get it spinning. The larger the rotational inertia, the more torque is required to get it spinning at a given angular acceleration. If each object were pushed with the same torque, the solid sphere would rotate the fastest, the solid cylinder would rotate the second fastest and the thin-wall hollow cylinder would rotate most slowly.