With the help of energy bands explain how conduction takes place in conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
On the basis of energy band materials are categorized as insulators, conductors and semiconductors.
Insulators: Substance as wood, glass, that do not permit the passage of current through them is termed as insulators. The valence band of these substances is full while the conduction band is fully empty. The forbidden energy gap among valence band and conduction band is very large (8ev) as demonstrated in the figure (a). Thus, a large amount of energy that is a very high electric field is needed to push the valence electrons to the conduction band. It is the reason, why such materials under ordinary conditions do not conduct at all and are designated like insulators.
Conductors: Substances as copper, aluminium and silver that permit the passage of current through them are conductors. The valence band of such substances overlaps the conduction band as demonstrated in figure (b). Because of this overlapping, a large number of free electrons are available for conduction. It is the purpose, why a slight potential difference applied across them causes a heavy flow of current throughout them.
Semiconductors: Substances as carbon, germanium and silicon that electrical conductivity lies in among the conductors and insulators are termed as semiconductors. The valence band of such substances is approximately filled, but the conduction band is approximately empty. The forbidden energy gap between valence and conduction band is very small (1ev) as shown in figure (c). Thus comparatively a smaller electric field is needed to push the valence electrons to the conduction band. It is the reason, why these materials under ordinary conditions do not conduct current and behaves as an insulator. Even though at room temperature, while some heat energy is imparted to the valence electrons, some of them cross over to the conduction band imparting minor conductivity to the semiconductors. Since the temperature is raised, more valence electrons cross over to conduction band and conductivity of the material raises. Therefore these materials have negative temperature co-efficient of resistance.
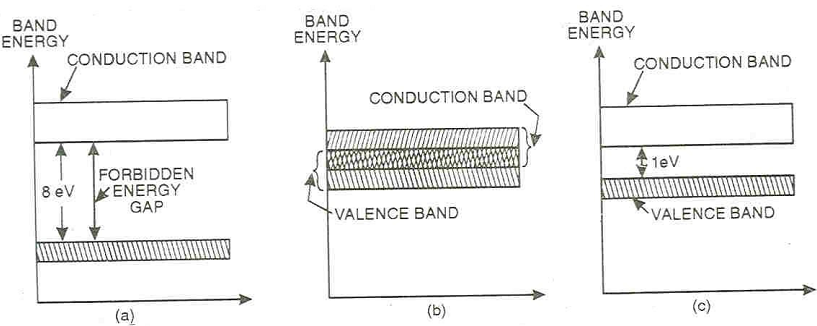
Energy Band Diagrams