Q. Explain Call and Return Statements?
CALL:
CALL X Procedure Call to procedure/function named X
CALL instruction causes the following to happen:
1. Decrement the stack pointer so that we won't overwrite last thing put on stack
(SP <---SP - 1)
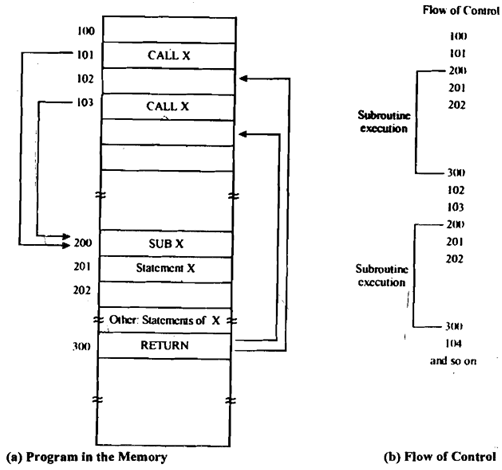
Figure: Call and Return Statements
2. The contents of PC that is pointing to NEXT instruction the one just after CALL is pushed onto stack and M [SP] <--- PC.
3. JMP to X address of the start of subprogram is put in PC register.This is all a jump does. So we go off to the subprogram though we have to remember where we were in calling program which means that we should remember where we came from so that we can get back there again.
PC <--- X
RETN:
RETN Return from procedure.
RETN instruction causes following to happen:
1. Pops the stack to produce an address/label.If correctly used, the top of the stack will comprise the address of next instruction after the call from that we are returning; it's this instruction with that we want to resume in calling program.
2. Jump to popped address it implies that put the address into PC register.
PC <--- top of stack value; Increment SP.