Explain acid and bases?
Acids and Bases : Some aqueous solutions, however, such as HCl, form an excess of hydrogen ions [ H+ ] and are called acids. Others, such as NaOH, form an excess of hydroxide ions [OH- ], and are called bases. Basic solutions are said to be alkaline.
Acids and bases are classified as either strong or weak, depending upon whether they are partially or fully ionized in solution. Weak acids, such as vinegar, have a sour taste. Weak bases taste bitter and feel soapy and slippery.
The pH Scale
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity of a solution. It is calculated from the concentration of the hydrogen H+ or hydronium ions H3O+ as follows:
pH = - log [H+] = - log [H3O+]
The equilibrium constant of water (Kw) is defined as follows:
Kw = [H3O+] [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14
A shorthand way to write the same information is
pH + pOH = 14
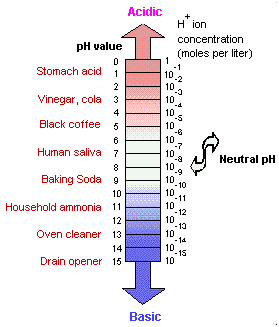
The pH of pure water and neutral solutions is 7; acidic solution values are less than 7. The pH values of alkaline solutions (bases) measure more than 7. Note that the pH scale is logarithmic, so that a pH of 4 is 100 times more acidic than a pH of 6. The pH in animal digestive tracts is controlled by secretion of certain glands, and varies from quite acidic, about 2 in the stomach, to somewhat alkaline in the intestines.
Certain dyes, such as phenolphthalein, can be used to give an approximate indication of pH. Specialized meters with probes that are dipped into a solution measure pH very accurately.
Salts and Buffers
Salts are formed by the reaction of acids and bases in water. They may be neutral, acidic or basic, depending upon the pH of their solutions.
Acid +base → salt +water
Because various chemical reactions that occur in living organisms proceed more readily at different pH levels, specialized tissues produce chemical substances called buffers. Buffers dissociate in aqueous solutions and combine with excess H+ or OH - to maintain a constant pH. Buffers are usually weak acids or weak bases, or salts of weak acids or weak bases.
An example of a buffer is carbonic acid H2 CO3 and its bicarbonate ion (HCO3 -), present in red blood cells: