Q. Explain about Roasting process?
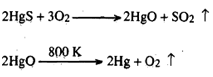
Roasting is the method of heating ores in the presence of excess air and involves oxidation. It is mainly applied to sulphide ores, which are converted lo oxides or sulphates. Various impurities like sulphides of antimony and arsenic also get oxidised' and volatilised. For example,
4FeS2+ 11O2--------------> 2Fe2SO3+ 8SO2
ZnS + 2O2------------------> ZnSO4
2ZnS + 3O2-------------------> 2ZnO+ 2SO2
2As2S3+ 9O2--------------> 2As2O3+ 6 So2
When cuprous sulphide is roasted in a partial supply of air, it is partially oxidised to Cu20,
Which is then reduced to copper by the residual cuprous sulphide:
2CuS2+ 3O2-------------> 2Cu2O + 2SO2
Cu2+ 2Cu2O-----------> 6CU + SO2
Sometimes, the oxides formed throughout roasting are unstable and decompose into elements at a moderately high temperature. For Illustration, in the roasting of cinnabar, the red sulphide ore of mercury, the oxide formed decomposes to provide the metal: