Q. What do you know about Radioactive Dating?
Ans.
Half-life measurements of radioactive elements in rocks and fossils can be used to determine the age of the specimen. One of the most common types of radioactive isotope dating uses carbon-14.
Carbon-14 is formed naturally in the atmosphere. It decays through β- emission to form nitrogen-14. The half-life of Carbon-14 is 5730 years.
When plants perform photosynthesis they take in carbon dioxide and water to make sugar and oxygen.
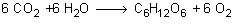
Some of the carbon dioxide the plant uses contains the isotope carbon-14.
When the plant dies or is harvested photosynthesis stops. It can no longer absorb any carbon-14. The decay of the isotope inside the dead plant continues a before. We can determine the age of a once-living plant by measuring the remaining radioactivity due to carbon-14.
We used the equation before
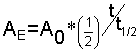
Let?s rearrange a little so that this equation makes sense for our radioactive dating problem.
Eventually we want to know t, the elapsed time. This will tell us the age of the dead plant.
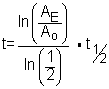
It is useful to note that the portion of the equation 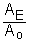 is just the fraction of the Carbon-14 remaining.
is just the fraction of the Carbon-14 remaining.
Although 5730 seems like a long time, it is actually pretty short in terms of half-lives. For this reason, Carbon-14 dating is most useful for recent dating -- objects 50,000 years or younger. Isotopes with a longer half-life are needed to date items that are older.