Explain ABO Blood Grouping System
As the name suggest, this is based on the presence or absence of 9 antigens A and B, on the surface of RBC. If either of these antigens is present on the surface of RBC, it can react with the corresponding antibody. Reaction between a blood group antigen and its corresponding antibody leads to clumping (agglutination) of RBCs. Hence, blood group antigens are known as 'agglutinogens' and the corresponding antibodies are known as 'agglutinins'.
Landsteiner found that if RBC of an individual carries a particular group antigen, RBC can circulate safely only if corresponding antibody is not present in the plasma of same individual. Hence a law was formulated by him, which states that 'if an antigen is present on the surface of RBC, the corresponding antibody would be absent in plasma'. Conversely, if an antigen is absent, the corresponding antibody is present. This law is good for ABO and not for Rh system.
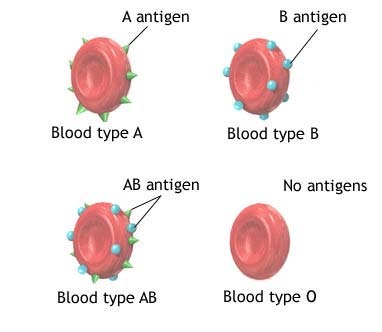
According to the ABO blood typing system, therefore, there are four different kinds of blood types: A, B, AB or O (null). What do they signify? Let's find out. If you belong to the blood group A, it means you have A antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and B antibodies in your blood plasma, as shown in Figure. If you belong to the blood group B, you have B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and A antibodies in your blood plasma. If you belong to the blood group AB, you have both A and B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells and no A or B antibodies at all in your blood plasma. If you belong to the blood group O (null), you have neither A or B antigens on the surface of your red blood cells, but you have both A and B antibodies in your blood plasma as you can see in the Figure.
The next question which might interest you is how do you find out which blood group one belongs to? The process is simple. First, the blood with three different reagents including either of the three different antibodies, A, B or Rh antibodies is mixed. Then one looks that in which mixtures agglutination has occurred? The agglutination indicates that the blood has reacted with a certain antibody and therefore is not compatible with blood containing that kind of antibody. If the blood does not agglutinate, it indicates that the blood does not have the antigens binding the special antibody in the reagent. If you know which antigens are in the person's blood, it's easy to figure out which blood group he or she belongs to. Further, you may have come across the terms 'universal Donor' and 'Recipients' in the context of blood transfusion.