Example which cause problems for some hidden-surface algorithms
Some special cases, which cause problems for some hidden-surface algorithms, are penetrating faces and cyclic overlap. A penetrating face occurs when polygon A passes through polygon B. Cyclic overlap occurs when polygon A is in front of polygon B, which is in front of polygon C, which is in front of Polygon A. Actually, we need only two polygons for cyclic overlap; imagine a rectangle threaded through a polygon shaped like the letter C so that it is behind the top of the C but in front of the bottom part. For the various hidden-surface methods we have presented, discuss whether or not they can handle penetrating faces and cyclic overlap.
(b) (i) Show that no polygon subdivision takes place in applying the binary space partition method to a convex object.
(ii) For the case of convex object compare the cost of the back-face removal method with that of the binary space partition method for a single view.
(iii) Suppose we wish to display a sequence of views of a convex object. How would the cost of using back-face removal compare to the binary space partition scheme?
(c) Modify the back-face algorithm for unifilled polygons so that instead of removing back faces it draws them in a less pronounced line style (e.g., as dashed lines).
(d) Test the painter's algorithm by showing several filled polygons with different interior styles and different states of overlap, entered in mixed order.
(e) Test the painter's algorithm by showing two houses composed of filled polygons with different interior styles. Select a view such that one house partially obscures the other house.
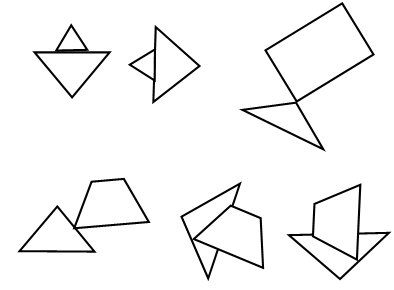
(f) Sketch the minimax boxes for the tangent polygons shown in figure. What conclusions can you make?