A 1500 gallon tank primarily holds 600 gallons of water along with 5 lbs of salt dissolved into it. Water enters the tank at a rate of 9 gal/hr and the water entering the tank has a salt concentration of 1/5 (1 + cos (t)) lbs/gal. If a well mixed solution goes away the tank at a rate of 6 gal/hr, how much salt is in the tank while it overflows?
Solution
Firstly, let's address the "well mixed solution" bit. It is the assumption that was mentioned earlier. We are going to suppose that the instant the water enters the tank this somehow immediately disperses evenly throughout the tank to provide a uniform concentration of salt into the tank at every point. Again, it will evidently not be the case in actuality, but it will permit us to do the problem.
Now, to set up the Initial Value Problem that we'll require to solve to get Q(t) we'll require the flow rate of the water entering as we've got that the concentration of the salt into the water entering when we've got that, the flow rate of the water leaving and the concentration of the salt into the water exiting but we don't have this yet.
Thus, we first require determining the concentration of the salt in the water exiting the tank. As we are assuming a uniform concentration of salt in the tank the concentration at some point into the tank and thus in the water exiting is specified by,
Concentration = Amount of salt in the tank at any time, t/Volume of water in the tank at any time, t
The amount at any time t is simple it's just Q(t). The volume is also pretty simple. We begin with 600 gallons and each hour 9 gallons enters and 6 gallons leave. Thus, if we use t in hours, each hour 3 gallons enters the tank, or at any time t there as 600 + 3t gallons of water into the tank.
Thus the Initial Value Problem for this condition is:
Q'(t) = 9 ((1/5)(1 + cos(t))) - 6 (Q(t)/(600 + 3t)), Q(0) = 5
Q'(t) = 9/5 ( 1 + cos (t)) - (2Q(t))/(200 + t), Q(0) = 5
It is a linear differential equation and this isn't too hard to solve hopefully. We will demonstrate most of the details, although leave the explanation of the solution process out. If you require a refresher on solving linear first order differential equations go back and see that section.
Q'(t) + ((2Q(t))/(200 + t)) = 9/5(1 + cos(t))
µ(t) = e∫(2/(200 + t)) dt = e2In(200 + t)) =(200 + t)2
∫((200 + t)2 Q(t))' dt = ∫(9/5(200+ t)2 (1 + cos(t))dt
(200 + t)2 Q(t) = 9/5((1/3 (200 + t)3) + ((200 + t)2 sin(t)) + (2 (200 + t) cos(t)) - (2 sin(t))) + c
Q(t) = 9/5((1/3 (200 + t)) + sin(t) + ((2cos (t))/(200 + t)) - ((2sin(t))/(200 + t)2)) +(c/(200 + t)2)
Thus, here's the general solution. Here, apply the initial condition to find the value of the constant, c.
5 = Q(0) = 9/5((1/3 (200) + (2/200)) + c/(200)2
C= - 4600720
Hence, the amount of salt into the tank at any time t as:
Q(t) = 9/5((1/3 (200 + t)) + sin(t) + ((2cos (t))/(200 + t)) - ((2sin(t))/(200 + t)2))-(4600720/(200 + t)2)
Now, the tank will overflow at t = 300 hrs. The amount of salt in the tank at that time is.
Q (300) = 279.797 lbs
There is a graph of the salt into the tank before it overflows.
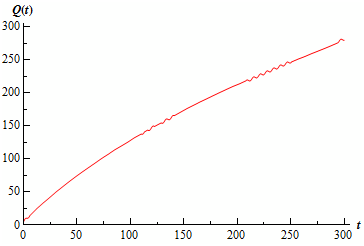
Remember that the complete graph must have small oscillations in it as you can notice in the range from 200 to 250. The scale of the oscillations though was small adequate that the program used to produce the image had trouble demonstrating all of them.
The work was a little messy along with that one, but they will frequently be that way so don't get excited regarding it. This first illustration also assumed that nothing would change during the life of the process. That, of course will generally not be the case.