Example of Introducing the Government- ACCOUNTING SYSTEM
So far there was no government in any of our stylized economies. Let us now introduce it. To begin with, our government engages in the following activities:
a. Imposes and collects taxes on personal income and corporate profits.
b. Employs labor, purchases goods and services from the corporate sector and using them as inputs 'produces' government services which are made available to the public without any explicit charges.
We set up the sector accounts as follows:
Production Sector

Government
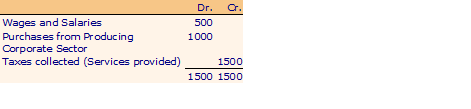
Household Sector
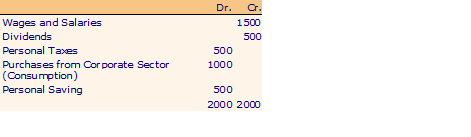
Savings and Investment

a. Total Value of Final Goods and Services:
1000 (Consumption) + 1000 (Investment) + 1500 (Government Services) = 3500
Here we treat government like any other producer whose output (government services) is bought by the 'public' by paying for it through taxes. All government services are treated as 'final output'.
b. Total Value Added:
1500 (Wages and Salaries) + (Gross Profits) 2000 = 3500
Once again government is treated as a producer which buys 'raw materials' and with the help of hired labor adds value to it.
c. c. Consumption + Investment + Government Expenditure:
1000 + 1000 + 1500 = 3500
Here we separate all governmental expenditures and add these to non-government expenditure on final output.
Conceptually, there is no difficulty in treating government like any other producer. However, a large part of government output is not sold through markets. Further, the government does not make its production decisions in response to market incentives like profitability. It cannot always identify which part of the tax revenue is financing which of its activities. Taxes people pay may not bear any relation with the amount of government services they consume. For all these reasons government expenditures are treated as a separate component of GNP as in (3) above. Government is treated in a dual role - producer of services and also as a collective 'consumer' on behalf of the society.
How about government enterprises like HMT, Modern Foods, etc.? They can be treated on par with non-government productive establishments since their output is sold in well-defined markets. (C + I) then includes output of consumption and investment goods by public and private sector enterprises. GNI includes factor incomes earned in these enterprises including any surpluses.
Thus for this example
GNP = C + I + G
where G denotes government expenditure.