Example of Bars of Varying Cross Section:
In the numerical example under consideration
δ = 750 × 300/( π/4) × 200 2 × 60 +750 × 400/(π/4) × 1352 × 60 + 750 × 200/(π/4) × 60 2 × 60 + 750 × 500/(π/4) × 100 2 × 60
+ 750/ (π/4) × 60 (300/2002+400/1352 + 200/602 + 500/1002) = 2.14865 mm
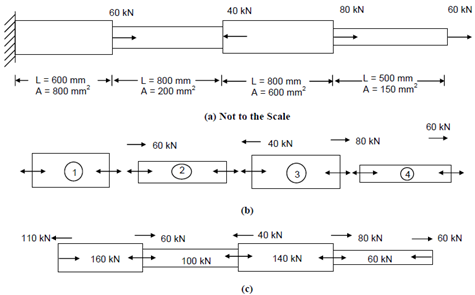
In the bar, display in Figure 16, the axial pull is applied at the ends and therefore the axial force in all the members is similar. On the bar, display in Figure 17(a), the external forces is applied at intermediate sections also. In such cases, the axial force in every member should be evaluated first, before any deformation calculations. This could be accomplished through considering equilibrium of each of the sections whereas external loads are applied. Though no external load has been prescribed at the LHS end, the support reaction has to be computed and taken as the external load. Equilibrium analysis could be simply carried out by treating each segment as a free body as display in Figure (b).
For instance, consider the equilibrium of the segment 4 in Figure (b). At the RHS end of the member a point load of 60 kN is applied. Therefore, for the member to be in equilibrium a force of - 60 kN should be applied at the RHS end of the member. Thus, the member is subjected to a tensile force of 60 kN which is represented through the internal arrows within accordance along with the sign conventions you have already learnt. Member 3 is pulled within a tensile force of 60 kN exerted through member 4 and further the external force of 80 kN also pulls the member in the similar direction, resulting in the member carrying a total tensile force of 140 kN. Proceeding therefore, the axial forces in all the members could be computed. To simplify the graphical representation we might display the member forces along along with external forces as shown in Figure(c).
Now let us compute the total elongation of the bar, taking the elastic modulus, E, as 200 kN/mm2.
Figure
δ = ∑ δi = ∑ Pi Li /Ai Ei
=(160 × 600/800 × 200)+ (100 × 800/200 × 200)+ (140 × 800/600 × 200)+(60 × 500/150 × 200)
= 0.6 + 2.0 + 0.9333 + 1.0
= 4.53333 mm.