Evaluate the principal stresses and principal planes:
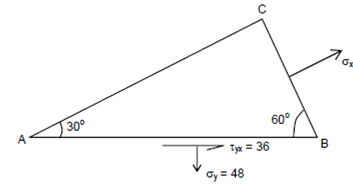
The state of stress at a point in a loaded solid is prescribed on two faces of an element whose shape is a triangular prism as display in Figure. Evaluate the principal stresses and principal planes.
Figure
Solution
Here, we have to first obtain the value of x and subsequent calculations will be a standard set.
Given σy = 48 MPa
τyx = 36 MPa ∴ τxy = - 36 MPa
σ30o = 60 MPa (aspect angle of plane BC is + 30o)
σ30° = (σx +σy/2) +(σx -σy/2) cos (2× 30°) +τxy sin (2 × 30°)
60 = (σx + 48/2) + (σx - 48/2) cos 60o + (- 36) sin 60o
60 = σx/2 + 24 +σx/2 cos 60° -24 cos 60° -36 sin 60°
i.e. 60 = σx/2 (1+ cos 60°) +24 -24 cos 60° -36 sin 60°
∴ σx =2/1+0.5 [60-24-(-24×0.5)-(-36)× 0.866]
= 2/1.5[79.177] = 105.57 MPa
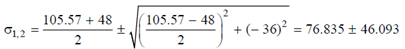
∴ σ1 = 76.835 + 46.093 =122.928 MPa
σ2 = 76.835 - 46.093 =30.742 MPa
Let the aspect angles of the principal planes be Φ
tan 2Φ = 2τxy/σx - σy = 2 × (- 36)/105.57 - 48 = -51.35° or 128.65°
Φ = - 25.675° or 64.325°
Substituting Φ = - 25.675o (or 2Φ = - 51.35o) in expression for σn
σn = (105.57 + 48/2 ) + (105.57 - 48/2) cos (- 51.35o ) - 36 sin (- 51.35o )
= 122.92 MPa
∴ Φ1 = - 25.675o and Φ2 = 64.325o