Evaluate the given definite integral.
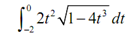
Solution
Let's begin looking at the first way of dealing along with the evaluation step. We'll have to be careful with this method as there is a point in the procedure where if we aren't paying attention we'll obtain the wrong answer.
Solution 1 :
First we'll need to compute the indefinite integral using the substitution rule. Note as well however, that we will continually remind ourselves that it is a definite integral by putting the limits on the integral at each of the step. Without the limits it's simple to forget that we contained a definite integral while we've gotten the indefinite integral computed.
In this case the substitution is,
u = 1 - 4t 3 du = -12t 2 dt ⇒ t 2 dt = - 1/12 du
Plugging this in the integral gives,
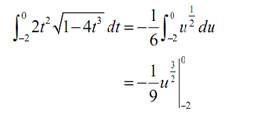
Notice as well that we didn't do the evaluation yet. It is where the potential problem arises along with this solution method. The limits specified here are from the original integral and therefore are values of t. We have u's in solution. We can't plug values of t in for u.
Therefore, we will have to go back to t's before we carry out the substitution. It is the standard step in the substitution procedure, but it is frequently forgotten while doing definite integrals. Note that in this case, if we don't go back to t's we will have small problem in that one of the evaluations will end up giving us a complex number.
Therefore, finishing this problem gives,
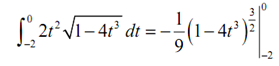
=-(1/9)-(-(1/9)(33)(3/2))
= (1/9)-( 33√33)-1)
Therefore, that was the first solution method. Let's see second method.
Solution 2 :
Note as well that this solution method isn't actually all that different from the first method. In this method while doing substitutions we desire to eliminate all the t's in the integral & write everything in terms of u.
While we say all here we actually mean all. In other terms, remember that limits on the integral are also values of t & we will convert the limits into u values. Converting the limits is fairly simple since our substitution will tell us how to associate t and u so all we have to do is plug in the original t limits into the substitution & we'll get the new u limits.
Following is the substitution (it's the same as the first method) as well as the limit conversions.
u = 1 - 4t 3 du = -12t 2 dt ⇒ t + dt = - 1/12 du
t = -2 ⇒ u = 1 - 4 ( -2)3 = 33
t = 0 ⇒ u = 1 - 4 (0)3 = 1
Now the integral is,
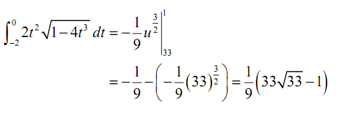
As along with the first method let's pause here a moment to remind us what we're doing. In this particular case, we've converted the limits to u's & we've also got our integral in terms of u's and therefore here we can just plug the limits directly into our integral. Note as well that in this case we won't plug our substitution back in. Doing it would cause problems as we would have t's in the integral and our limits would be u's. Following is the rest of this problem.
We exactly got the similar answer & this time didn't have to worry about going back to t's in our answer.
Therefore, we've seen two solution techniques for calculating definite integrals which require the substitution rule. Both are valid methods and each has their uses. We will be using the second completely however as it makes the evaluation step a little easier.