Evaluate the acceleration of the three weights:
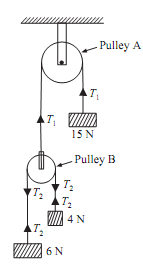
A system of weight connected by the string passing over pulleys A and B is shown in figure given below. Find out acceleration of the three weights. Assume the weightless string and ideal condition for the pulleys.
Sol: As strings are weightless and ideal conditions prevail, thus the tensions in string passing over pulley A will be same. The tensions in string passing over pulley B will be same. But tensions in the strings passing over pulley A and over pulley B will be different as shown in the given figure.
Let T1 = Tension in string passing over pulley A
T2 = Tension in string passing over pulley B
One end of string passing over pulley A is connected to the weight 15N, and other end is connected to pulley B. As weight 15N is more than weights (6 + 4 = 10N), thus weight 15N will move downwards, while pulley B will move upwards. The acceleration of weight 15N and of pulley B will be same.
Let, a = Acceleration of block 15N in the downward direction1 = Acceleration of 6N downward with respect to the pulley B.
Then acceleration of weight 4N with respect to the pulley B = a1 in upward direction.
The absolute acceleration of weight 4N,
= Acceleration of 4N with respect pulley B + Acceleration of pulley B. = a1 + a (upward)
(as both the acceleration are in upward direction, total acceleration will be the sum of the two accelerations)
Absolute acceleration of weight 6N,
= Acceleration of 6 with respect to pulley B + Acceleration of pulley B.
= a1 - a (downward)
(As a1 is acting downward while a is acting upward. Thus total acceleration in downward direction)
Consider motion of weight 15N Net downward force = 15 - T1
Using F = ma,
15 - T1 = (15/9.81)a ...(1)
Consider motion of weight 4N
Net downward force = T2 - 4
Using F = ma,
T2 - 4 = (4/9.81)(a + a1) ...(2)
Consider the motion of weight 6N
Net downward force = 6 - T2
Using F = ma,
6 - T2 = (6/9.81)(a1 - a) ...(3)
Consider motion of pulley B,
T1=2T2 ...(4)
Adding equation (2) and (3)
2 = (4/9.81)(a + a1) + (6/9.81)(a1 - a)
9.81 = 5a1 - a ...(5)
Multiply equation (2) by 2 and put value of equation (4),
T1 - 8 = (8/9.81)(a1 + a) ...(6)
Add equation (1) and (6), we get
15 - 8 = (15/9.81)a + (8/9.81)(a1 + a)
23a + 8a1 = 7 X 9.81 ...(7)
Multiply equation (5) by 23 and add with equation (7),
a1 = 2.39m/sec2 .....ANS
Putting value of a1 in equation (5),
a = 2.15m/sec2 ....ANS
Acceleration of weight 15N = a = 2.15m/sec2 ......ANS
Acceleration of weight 6N = a = 0.24m/sec2 .......ANS
Accelerationofweight 4N = a = 4.54m/sec2 .......ANS