1. Estimating Women's Labor Supply
a. The following regression was run for an estimate of the current women's labor supply curve:
Where
hi = hours of labor supplied by female worker i (with mean = 32)
w = wage earned by female worker i (with mean = 13)
Vi = non-labor income by female worker i (with mean = 50)
Zi = other control variables.
The coefficients were estimated to be b = 1.05, g = -0.4, and h = 0.004. What is the elasticity of the substitution-effect?
b. Using the values in (d), what is the elasticity of the supply curve for women?
c. What does this elasticity mean?
d. Is this elasticity giving an relatively elastic or inelastic supply curve?
2. Question on Children, Fertility, and Labor Supply
a. Graph an increase in the price of children when children are an inferior good.
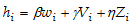
b. Did Malthus propose that children are normal or inferior goods?
c. Graph an increase in the price of children when children are a normal good.
d. Does the empirical evidence provided (from both "Wage-based" and "Income-based" measures) suggest that children are normal goods or inferior goods? Why or why not?