Equilibrium National Income in a Frugal Economy
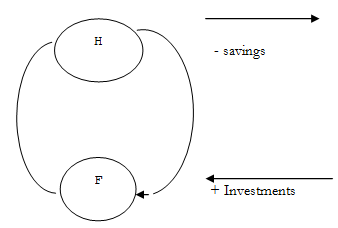
Saving and investment are examples of two categories of expenditure called withdrawals and injections. A WITHDRAWAL is any income that is not passed on in the circular flow. Thus if households can earn income and not spend it on domestically produced goods and services, this is a withdrawal from the circular flow. Similarly, if firms receive money from the sale of goods and do not distribute it as payments to factors, this is a withdrawal from the circular flow.
AN INJECTION is an addition to the incomes of domestic firms that does not arise from the expenditure of domestic households or arise from the spending of domestic firms.
The effects of withdrawals and injections is to interfere with Equilibrium income. Withdrawals by reducing expenditure exert a contractionary force on national income. If, for example, households decide to increase their savings and correspondingly reduce the amount they used to spend buying consumption goods from firms, this reduces the incomes of firms, and reduces the payments they will make to factors of production. Injections, by raising expenditure, exert an expansionary force on national income. If, for example, firms sell machines to other firms, their incomes and payments to household for factor services will rise without there having been an increase in household expenditure.
Thus for equilibrium National Income to exist, firm spending should be equal to firm receipts. Thus, denoting consumption by C, saving by S and Investment by I, there is equilibrium if:
C + S = C + I
Or
S = I
i.e. there is equilibrium when savings are equal to investments.
To measure the National Income in a frugal economy, through the output and Expenditure approach, the National Income Accountant includes production of goods for inventories as part of total expenditure since the firm certainly spends money on the factor services necessary to produce goods for its own inventories. The accountant calculates the economy's total output as the actual expenditure on final goods and services sold, plus the market value of final commodities currently produced and added inventories. This definition makes total expenditure the same thing as the value of all final commodities produced and thus ensures that the measured value of expenditure is identical with the value of total output in any economy.