Equilibrium in both the goods and in the money market
|
If both the goods- and the money markets are to be in equilibrium...
...if P increases, Y must fall and R increase ...
...if P decreases, Y must increase and R fall
|
For a given P, we can use IS and LM curves to find equilibrium values of interest rate and GDP. Though we can also determine how the equilibrium values of R and Y depend on P.
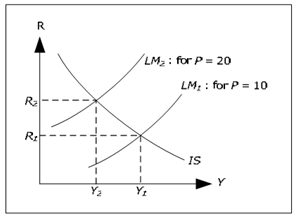
Figure: How P affects the equilibrium in the goods and money market
LM1 is the LM curve when P = 10, whereas LM2 is the LM curve when P = 20. LM2 is above LM1. If Y1 and R1 are the equilibrium values when P = 10 and Y2 and R2 are equilibrium value when P = 20, we see that Y2< Y1 and R2> R1.
We may draw the following conclusion. When prices increase, GDP should fall and interest rates should increase if both the goods and money market is to be in equilibrium. Economic intuition is something like following:
1. When P increases, demand for money increases
2. When MD increases, interest rate increases
3. When R increases, investments fall
4. When I falls, GDP falls
Of less significance is the following point: when GDP falls in step 4, MD will fall slightly - however not as much as it increased in step 1. So interest rate will decline slightly compared to the level in step 2.
More significantly, we no longer have a unique equilibrium from money market and goods market. As there is a unique LM curve for each value of P, there is an equilibrium (in both markets) for each value of P.
|
The AD curve shows all combinations of P and Y where the goods and themoney markets are both in equilibrium. The AD curve slopes downwards.
|
From the section above, we know that Y should fall if P increases if we want both markets to remain in equilibrium. In this unit we derive the exact relationship between P and Y when both markets are in equilibrium.
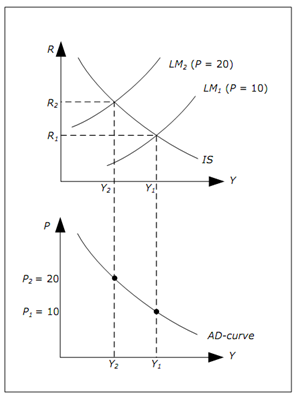
Figure: Derivation of the AD curve
We can explain our derivation using the diagram above.
1. First select P1 = 10 and P2 = 20 in the lower diagram.
2. Draw IS curve in the upper diagram and two LM curves - the one corresponding to P = 20 should be above the one for P = 10.
3. Identify resulting GDP in the upper graph for both prices - the highest level of GDP is associated with lower of the prices.
4. Extend these levels of GDP to lower graph. This will lead to two points in the lower graph.
5. Keep on doing this with other prices. Resulting downward sloping curve in the lower graph is known as the AD-curve.
Keep in mind that both goods market and money market is in equilibrium at all points on the AD curve. Thus AD-curve alone can't identify to which point the economy will move.