Equilibrium in a single market model
A single market model has three variables: the quantity demanded of the commodity (Qd), the quantity supplied of the commodity (Qs) and the price of the commodity (P). equilibrium is assumed to hold in the market when the quantity demanded (Qd) = Quantity Supplied (Qs) . It is assumed that both Qd and Qs are functions. A function such as y = f (x) expresses a relationship between two variables x and y such that for each value of x there exists one and only one value of y. Qd is assumed to be a decreasing linear function of P which implies that as P increases, Qd decreases and Vice Versa. Qs on the other hand is assumed to be an increasing linear function of P which implies that as P increases, so does Qs.
Mathematically, this can be expressed as follows:
Qd = Qs
Qd = a - bP where a,b > 0. ............................(i)
Qs = -c + dp where c,d >0. ...........................(ii)
Both the Qd and Qs functions in this case are linear and can be expressed graphically as follows:
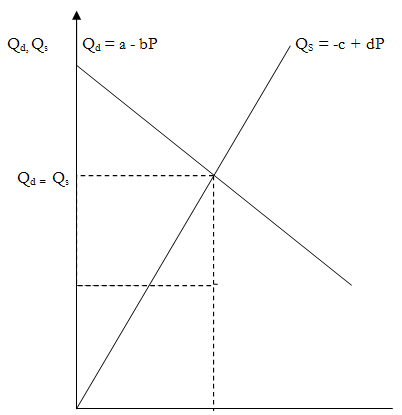
Once the model has been constructed it can be solved.
At equilibrium,
Qd = Qs
\a - bP = -c + dP
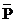 = a + c
= a + c
b + d
To find the equilibrium quantity 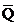 , we can substitute into either function (i) or (ii).
, we can substitute into either function (i) or (ii).
Substituting 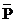 into equation (i) we obtain:
into equation (i) we obtain:
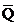 = a - b (a+c) = a (b+d) - b (a+c) = ad -bc
= a - b (a+c) = a (b+d) - b (a+c) = ad -bc
b + d b + d b + d
Taking a numerical example, assume the following demand and supply functions:
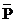 = 100 - 2P
= 100 - 2P
Qs = 40 + 4P
At equilibrium, Qd = Qs
100 - 2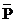 = 40 + 4
= 40 + 4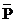
6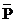 = 60
= 60
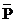 = 10
= 10
Substituting P = 10, in either equation.
Qd = 100 - 2 (10) = 100 - 20 = 80 = Qs
A single market model may contain a quadratic function instead of a linear function. A quadratic function is one which involves the square of a variable as the highest power. The key difference between a quadratic function and a linear one is that the quadratic function will yield two solution values.
In general, a quadratic equation takes the following form:
ax2 + bx + c = 0 where a ¹ 0.
Its two roots can be obtained from the following quadratic formula:
X1, X2 = -b + √( b2 - 4ac)
2a
Given the following market model:
Qd = 3 - P2
2 = 6P - 4
At equilibrium:
3 - P2 = 6P - 4
P2 + 6P - 7 = 0
Substituting in the quadratic formula:
a =1, b = 6, c = -7
= - 6 +Ö 62 - 4 (1 x - 7)
2 x 1
= 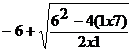
P = 1 or -7 (ignoring -7 since price cannot be negative)
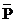 = 1
= 1
Substituting 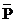 = 1 into either equation:
= 1 into either equation:
Qd = 3 - (1)2 = 2 = Qs
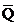 = 2
= 2