EPISTASIS
Epistasis is the phenomenon of masking or suppressing the expression of a gene by another non allelic gene. The gene which suppresses the expression of a non allelic gene is known as epistasis gene.
The gene or locus which is suppressed by the presence of non allelic gene is termed as hypostatic gene.
Epistasis is of following types - dominant and recessive.
Dominant Epistasis (12 : 3 : 1)
The dominant gene at one locus suppresses the expression of another gene at a different locus regardless of its allelic condition (dominant or recessive). The F ratio is generally 12 : 3 : 1.
Example :- 1
Fruit Colour in Cucurbita pepo. In Summer Squash or Cucurbita pepo, there are three types of fruit colour- yellow, green and white. White colour is dominant over other colours while yellow is dominant over green. Yellow colour is formed only when the dominant epistatic gene is represented by its recessive allele (w). When the hypostatic gene is also recessive (y), the colour of the fruit is green.
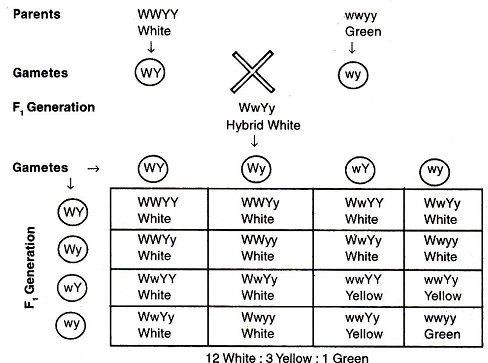
Inheritance of fruit colour in Cucurbita pepo due to dominant epistasis.
White fruit - W-Y-, W-yy
Yellow fruit - wwY- Green fruit - wwyy
A cross between a pure breeding white Summer Squash WWYY with a pure breeding green Summer Squash wwyy yields white fruits in the F generation. On inbredding, the F yellow generation comes to have 12 white fruits : 3 fruits : 1 green fruit.
Example :- 2
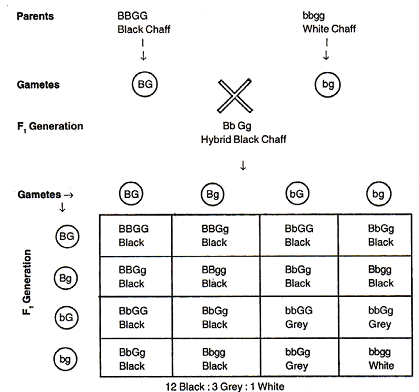
Chaff Colour in Oat. In Oat, the chaff can have three colours - black, grey and white. Black colour (B-) is dominant over all others. In its absence grey colour (bbG-) is dominant over white (bbgg). The dominant gene of black colour (B) is epistatic over the alleles for grey and white chaff colour (G-and gg). When a pure black chaff producing plant (BBGG) is crossed with a pure white chaff producing plant (bbgg) the hybrids of F1 generation plants have black chaff (BbGg). On self breeding the resultant plants of F2 generation have three types of chaff in the ratio of 12 black : 3 grey : 1 white.