Eliminating data hazards:
Forwarding
NOTE: In the following instance, computed values are in bold, whereas Register numbers are not.
Forwarding involves adding output data into a previous stage of the pipeline. For example, let's assume we desire to write the value 3 to register 1, (which already contains a six), and then add 7 to register 1 and hold the result in register 2, for instance
Instruction 0: Register 1 = 6
Instruction 1: Register 1 = 3
Instruction 2: Register 2 = Register 1 + 7 = 10
Following execution, register 2 would contain the value 10. Though, if Instruction 1 (write 3 to register 1) does not fully exit the pipeline before Instruction 2 begins execution, it means that Register 1 does not contain the value 3 when Instruction 2 performs its addition operation. In such type of event, Instruction 2 adds 7 to the old value of register 1 (6), and so register 2 would contain 13 instead for example Instruction 0: Register 1 = 6
Instruction 1: Register 1 = 3
Instruction 2: Register 2 = Register 1 + 7 = 13
This error takes place because before Instruction 1 has committed/stored Instruction 2 reads1 Register the result of its write operation to Register 1. Thus when Instruction 2 is reading the contents of Register 1, register 1 still contains 6, not 3.
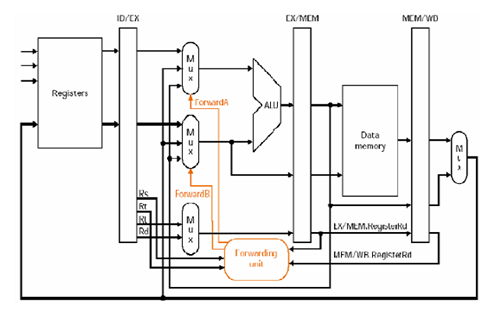
Forwarding (described below) helps right such errors by depending on the fact that the output of Instruction 1 (which is 3) may be utilized by subsequent instructions before the value 3 is committed to/stored in Register 1.
Forwarding is implemented by putting back the output of an instruction into the previous stage(s) of the pipeline as soon as the output of that instruction is available. Forwarding applied to our instance means that we do not wait to commit/store the output of Instruction 1 in Register 1 (in this instance, the output is 3) before making that output accessible to the subsequent instruction (in this particular case, Instruction 2). The effect is that Instruction 2 uses the right (the more recent) value of Register
1: the commit/store was made instantly and not pipelined.
With forwarding enabled, the ID/EX[clarification needed] stage of the pipeline now has 2 inputs: the value read from the register mention (in this instance, the value 6 from Register 1), and the new value of Register 1 (in this instance, this value is 3) which is sent from the next stage (EX/MEM)[clarification needed]. Additional control logic is utilized to determine which input to use.