What are the different elements in Functions points?
1) Internal Logical Files (ILF):
Following are some points to be noted for ILF:-
- The ILF are logically related data from user point of view.
- They reside in the Internal Application boundary and are maintained through elementary process of application.
- The ILF may have maintenance screen or probably not.
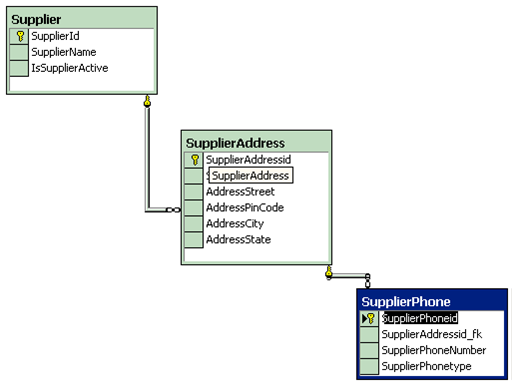
Figure: - Supplier ER database diagram
2) External Interface file (EIF):
They are logically related data from the user point of view.
- The EIF reside in the external application boundary.
- The EIF is used only for the reference purpose and are not maintained by the internal application.
- The EIF is maintained by external application.
3) Record Element Type (RET):
Following are some points to be noted for RET:
- The RET are sub-group element data of ILF or EIF.
- When there is no sub-group of ILF then count the ILF itself as one RET.
- A group of RET within the ILF are logically related, most probably with a parent Child relationship. For e.g.: - The Supplier had multiple addresses and each address can have multiple phone numbers. Therefore the Supplier, Supplier Address & Supplier phone numbers are RET.
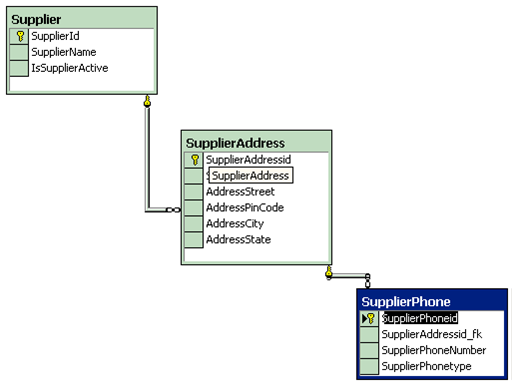
Figure: - Whole supplier is one ILF.
4) DET (Data element types)
Following are some points to be noted for DET counting:-
- Each DET must be User recognizable. For e.g. in the above given figure we have kept auto increment field (Supplierid) for primary key. The Supplierid field from the user point of view never exists at all, it is only from the software designing aspect, so does not qualifies for DET.
- The DET must be non-recursive field in ILF. The DET should not repeat in the same ILF again, it should be counted only once.
- They Count foreign keys as one DET. "Supplierid" does not qualifies as DET but its relationship in the "supplieraddress" table is counted as DET. Therefore "Supplierid_fk" in supplieraddress table is counted as DET. The same holds true for the "Supplieraddressid_fk".
5) File Type Reference (FTR)
Following are some points to be noted for FTR:-
- The FTR is a files or data referenced by a transaction.
- The FTR should be ILF or EIF. So count every ILF or EIF read during process.
- If the EP is maintaining an ILF then count it as FTR. Therefore by default you will always have one FTR in any EP
6) External Input (EI):
Following are some points to be noted for EI:-
- It is a dynamic elementary process in which data is received from an external application boundary. For e.g.: - the User Interaction Screens, when data comes from the User Interface to Internal Application.
- The EI may maintain ILF of the application, but it is not compulsory rule. For e.g.: - The calculator application does not maintain any data, but still the screen of calculator will be counted as EI.
- Most of time the User Screens will be EI, again no hard and fast rule. For e.g.: - An import batch process running from the command line does not have screen, but still should be counted as EI as it helps passing data from the External Application Boundary to the Internal Application Boundary.
7) External Inquiry (EQ):
Following are some points to be noted for EQ:
- It is a dynamic elementary process in which the result data is retrieved from one or more ILF or EIF.
- In this EP some of the input request has to enter the application boundary.
- The Output results exits the application boundary.
- The EQ does not contain any derived data. The Derived data means any complex calculated data. The Derived data is not just mere retrieval but are combined with an additional formula to generate results. The Derived data is not a part of the ILF or EIF, they are generated on fly.
- The EQ does not update any ILF or EIF.
- The EQ activity must be meaningful from user perspective.
- The EP is self contained and leaves the business in a consistent state.
- The DET and processing logic is different from other EQ's.
- The Simple reports form good base as EQ.