Q. Electronic Configuration and Position in Periodic Table?
The outstanding feature of the actinide and lanthanide elements is the great similarity in chemical and physical properties which they show within each series. Reason for this unique nature of these elements lies in their electronic configuration.
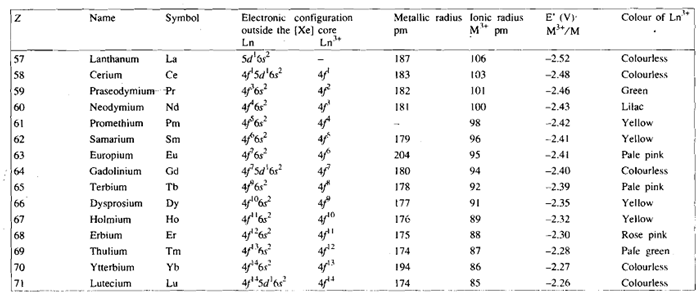
You know that lanthanum, the element preceding the lanthaniqs in the periodic table, has the electronic configuration [xe] 5d16s2. Like lanthanum, the lanthanides also exhibit the stable oxidation state of +3. It is, thus, expected that in these elements the successive electrons will be filled in the 4 orbitals, thereby the elements can have the electronic configuration from [xe]4f15d1 6s2 to [Xe]4f14 5d1 6s2 . The actual ground state electronic configurations of lanthanide elements have been evaluate by atomic spectroscopy and are given in Table. You will see from the Table that there is an electron in 5d orbital only in Gd, Ce and Lu, in all other elements this electron is shifted to the 4f orbital. This kind of shuttling of electrons can be understood in terms of the comparable energies of the Sd and 4f orbitals. Whether there is an electron in 5d orbital or not, is of little importance due to the lanthanides mostly form ionic compounds in +3 oxidation state and the electronic configuration of M3+ ions varies in a regular manner from [xe]4f1 for Ce3+ to [xe]4f14 for LU3+, as shown in Table.
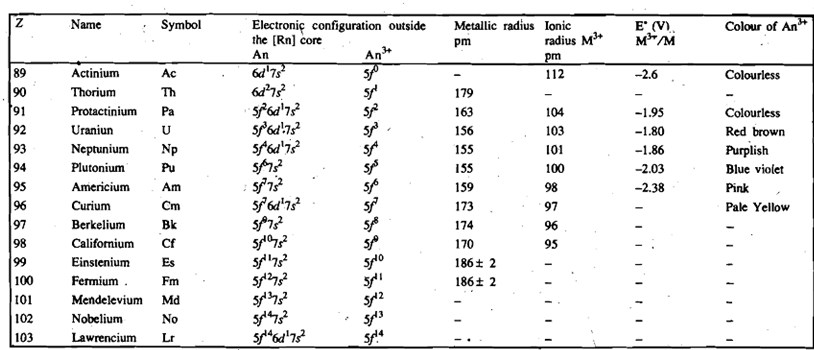
The ground state electronic configuration of actinium, [Rn] 6d1 7s2 is same as that of lanthanum and indeed the two elements possess similar chemical properties. The electronic configurations of the elements that follow actimum are not identified precisely; these are less certain than those of the lanthanide elements. The difference in energy between 5f and 6d orbitals in the beginning of the actinide series is less than that between the 4f and 5d orbitals for the lanthanides. Therefore, both Sf and 6d orbitals are involved in accommodating successive electrons. Thus the filling of Sf orbitals in actinides (Table 13.2) is not quite as regular as the filling of the 4f orbitals in the case of the lanthanides. Later, however, the 5f orbitals become more stable, i.e., by the time plutonium and subsequent members of the series are reached, the 5f orbitals seem clearly to be of lower energy than the 6d orbitals, and so the electrons preferably fill the former.