Q. Efficiency - Metrics for performance evaluation?
The other significant metric employed for performance measurement is efficiency of parallel computer system it implies that how resources of parallel systems are being utilized. This is termed as degree of effectiveness. The efficiency of program on parallel computer with k processors may be stated as ratio of relative speed up achieved whilst shifting load from single processor machine to k processor machine where multiple processors are being used for achieving result in a parallel computer. This is indicated by E(k).
Ek is defined in this manner:
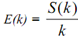
The value of E(k) is directly proportional to S(k) while inversely proportional to number of processors used for performing computation. The relation between E(k) versus Number of processors is displayed in Figure.
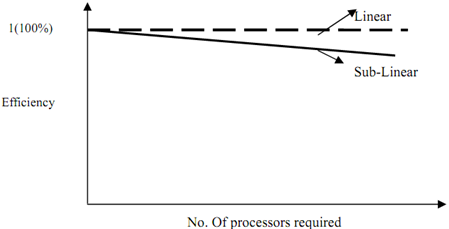
Figure: Efficiency vs. Number of Processors
Assuming we have multiplication problem as discussed above with k processors then efficiency is as under:
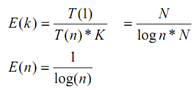
Supposing we have X processors it implies that X < K as well as we have to multiply n numbers in such a condition processors may be overloaded or might have a few overheads. Then efficiency is as under:
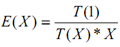
Now value of T(X) has to be calculated. As we have n numbers as well as we have X processors consequently firstly every processor will multiply n/X numbers as well as consequently process X partial results on X processors according to method discussed in Figure. Time complexity is equivalent to sum of time to calculate multiplication of k/X numbers on every processor it implies that O(k/X) as well as time to calculate solution of partial results it implies that log (X)
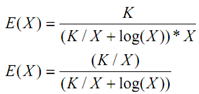
Dividing by X/K we get
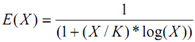
It can be concluded from above statement if N is fixed then efficiency it implies that E(X) will reduce like value of X raises and becomes equal to E(N) in case X=N. In the same way , if X is fixed then efficiency it implies that E(X) will raise as value of X it implies that the number of computations raises. The other performance metrics include standard metrics such MIPS and Mflops. The term MIPS (Millions of Instructions Per Second) denotes the instruction execution rate. Mflops (Million of Floating Point Operations per Second) denotes floating-point execution rate.