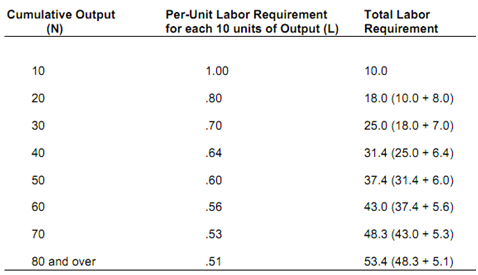
Dynamic Changes in Costs: The Learning Curve
* The learning curve measures impact of worker's experience on costs of production.
* It describes relationship between a firm's cumulative output and amount of inputs required to produce a unit of output.
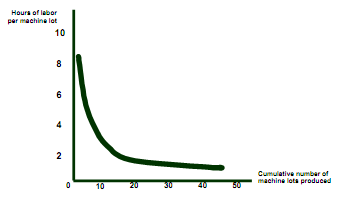
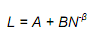
* If N=1
- L equals A + B and this measures labor input to produce the first unit of output
- If β = 0
- Labor input remains constant as the cumulative level of output increases, cause there is no learning.
* If β > 0 and N increases
- L approaches A, and A represent minimum labor input unit of output after all learning has taken place.
- The larger β:
- The more important becomes the learning effect.
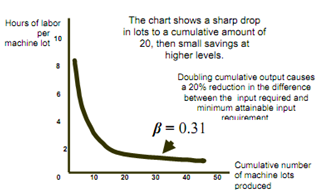
* Observations
1) New firms can experience learning curve and not economies of scale.
2) Older firms have small gains from learning.
Economies of Scale Versus Learning
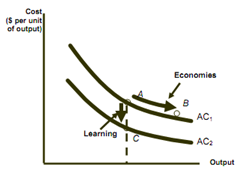
* The learning curve implies:
1) The requirement of labor falls per unit.
2) Costs will be high at 1st and then will fall with learning.
3) After eight years the labor requirement will be 0.51 and per unit cost will be ½ what it was in the 1st year of production?