Draw the schematic circuit of an Analog to Digital converter using Voltage-to Frequency conversion and explain its principle of operation. Draw its relevant Waveforms.
Ans:
Analog to Digital Converter Using Voltage-to-Frequency Conversion: An analog voltage can be converted into digital form by producing pulses whose frequency is proportional to the analog voltage. These pulses are counted by a counter for a fixed duration and the reading of the counter will be proportional to the frequency of the pulses and hence to the analog voltage.
A voltage-to-frequency converter is shown in Fig. (a). The analog voltage Va is applied to an integrator whose output is applied at the inverting input terminal of a comparator. The non-inverting input terminal of the comparator is connected to a reference voltage -VR.
Initially, the switch S is open and the voltage vo decreases linearly with time (vo = Vat/τ ) which is shown in Fig. 10(b). When the decreasing vo reaches -VR at t =T, the comparator output VC goes HIGH. This is used to close the switch S through a monostable multivibrator. When the switch S is closed, the capacitor C discharges, thereby returning the integrator output vo to 0. Since the pulse width of the waveform VC is very small, therefore, a monostable multivibrator is used to keep the switch S closed for a sufficient time to discharge the capacitor completely. The rate at which the capacitor discharges depends upon the resistance of the switch.
Let the pulse width of the monostable multivibrator be Td. Therefore, the switch S remains closed for Td after which it opens and vo starts decreasing again.
If the integration time T >> Td, the frequency of the waveforms Vo and VC is given by
f = 1/( T + Td) ≅ 1/T = (1/ τ) (Va/VR)
Therefore we get an output waveform whose frequency is proportional to the analog input voltage. Using the voltage-to-frequency (V/F) converter an A/D converter is demonstrated in Fig.(c). The output of the voltage-to-frequency converter is applied at the clock (CK) input of a counter throughout an AND gate. For a fixed time interval T1, the AND gate is enabled. The reading of the counter at t = T1 is specified by
n = fT1 = (1/ τ) (Va/VR) T1 that is proportional to Va
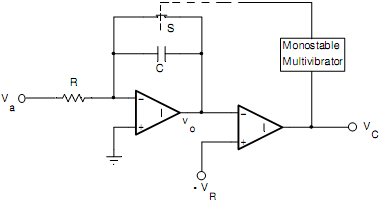
Fig.(a) Logic diagram of Voltage-to-Frequency Converter
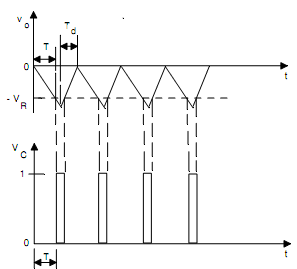
Fig.(b) Waveforms of Voltage-to-Frequency Converter
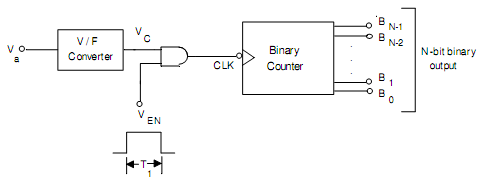
Fig.(c) Schematic circuit of A/D converter using a V/F converter