In any singly linked list, each of the elements contains a pointer to the next element. We have illustrated this before. In single linked list, traversing is probable only in one direction. Sometimes, we ought to traverse the list in both of the directions to improve performance of algorithms. To enable this, we require links in both the directions, i.e., the element has to have pointers to the right element in addition toto its left element. This type of list is called asdoubly linked list.
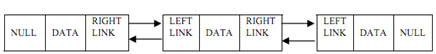
Figure: A Doubly Linked List
Doubly linked list is described as a collection of elements, each of element consisting of three fields:
Ø pointer to left element,
Ø data field, &
Ø pointer to right element.
Left link of the leftmost element is set to NULL that means that there is no left element to that. And, right link of the rightmost element is set to NULL that means that there is no right element to that.
ALGORITHM (Creation)
Step 1 begin
Step 2 define a structure ELEMENT with fields
Data
Left pointer
Right pointer
Step 3 declare any pointer by name head and using (malloc()) memory allocation function allocate space for one element & store the address in head pointer
Head = (ELEMENT *) malloc(sizeof(ELEMENT))
Step 4 read the value for head->data head->left = NULL
head->right = (ELEMENT *) malloc(size of (ELEMENT))
Step 5 repeat step3 to create needed number of elements
Step 6 end
Program demonstrated the creation of a Doubly linked list.
/* CREATION OF A DOUBLY LINKED LIST */
/* DBLINK.C */
# include
# include
structdl_list
{
int data;
structdl_list *right;
structdl_list *left;
};
typedefstructdl_listdlist;
voiddl_create (dlist *);
void traverse (dlist *);
/* Function creates simple doubly linked list */
voiddl_create(dlist *start)
{
printf("\n Insert values of element -1111 to come out : ");
scanf("%d", &start->data);
if(start->data != -1111)
{
start->right = (dlist *) malloc(sizeof(dlist));
start->right->left = start;
start->right->right = NULL;
dl_create(start->right);
}
else
start->right = NULL;
}
/* Display the list */
void traverse (dlist *start)
{
printf("\n traversethe list usingright pointer\n");
do {
printf(" %d = ", start->data);
start = start->right;
}
while (start->right); /* Demonstrates value of last start only one time */
printf("\n traversethe listusing left pointer\n");
start=start->left;
do
{
printf(" %d =", start->data);
start = start->left;
}
while(start->right);
}
{
dlist *head;
head = (dlist *) malloc(sizeof(dlist));
head->left=NULL; head->right=NULL; dl_create(head);
printf("\n created doubly linked list is as ");
traverse(head);
}