Direct and Indirect Semiconductors
1) In a common quantitative calculation of band structures, the wave function of a single electron traveling by a perfectly periodic lattice is assumed to be in the type of a plane wave moving in the x-direction (say) with propagation constant k, as well called a wave vector.
2) In quantum mechanics, the electron momentum can be provided by p= hk.
3) The wave function that is space dependent for the electron is ΨK (X) = U (Kx,x) ejK,x in which the function U(Kx,x) modulates the wave function as per to the periodicity of the lattice.
4) Allowed values of energy, where as plotted as a function of k, gives the E-k diagram.
5) As the periodicity of most lattices is different in several directions, the E-k diagram is a complex surface that is to be visualized in three dimensions.
6) Direct band gap semiconductor: the minima of the conduction band and the maxima of the valence band take place at the same value of k => an electron creating the smallest energy transition from the conduction band to the valence band can do so with no a change in k (and, the momentum).
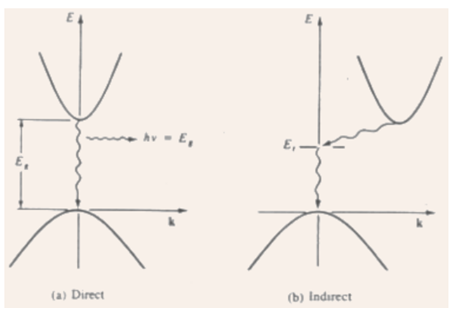
Figure: Direct and indirect transition of electrons from the conduction band to the valence band: (a) direct - with accompanying photon emission, (b) indirect via defect level.
7) Indirect band gap semiconductor: the minima of the conduction band and the maxima of the valence band take place for different values of k, so, the smallest energy transition for an electron needs a change in momentum.
8) Electron that falling from conduction band to an empty state in valence band => recombination.
9) Recombination possibility for direct band gap semiconductors is much higher than as compared to that for indirect band gap semiconductors.
10) Direct band gap semiconductors give up the energy released throughout this transition (=Eg) in the form of light => employed for optoelectronic applications (e.g., LEDs and LASERs).
11) Recombination in indirect band gap semiconductors takes place by some defect states within the band gap, and the energy is released in the type of heat given to the lattice.