Djikstra's algorithm (named after it is discovered by Dutch computer scientist E.W. Dijkstra) resolves the problem of finding the shortest path through a point in a graph (the source) to a destination along non-negative weight edge.
It turns out that one can determine the shortest paths from given source to all vertices (points) into a graph in the similar time. Therefore, this problem is sometimes called the single-source shortest paths problem. Dijkstra's algorithm is greedy algorithm, which determine shortest path among all pairs of vertices within the graph. Before defining the algorithms formally, let us study the method through an example.
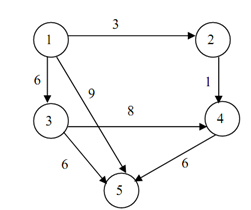
Figure: A Directed Graph with no negative edge(s)
Dijkstra's algorithm has two sets of vertices that are following:
S = set of vertices whose shortest paths from the source have been determined already
Q = V-S is the set of remaining vertices.
The other data structures required are following:
d is array of best estimates of shortest path to each of the vertex from the source
pi is array of predecessors for each of vertex. predecessor is an array of vertices to which shortest path has already been find out.
The fundamental operation of Dijkstra's algorithm is edge relaxation. If there is any edge from u to v, then the shortest known path from s to u can be extended to a path from s to v by adding up edge (u,v) at the end. This path will have length d[u]+w(u,v). If this is less than d[v], we can replace the current value of d[v] along with new value.
The predecessor list is an array of indices, one for each vertex of any graph. Each vertex entry has the index of its predecessor in a path through the graph.