Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are based on a grouping of the conventional idea of data hashing with public key-based encryption. Most hash functions are like to encryption functions. In fact, some hash functions are just a little modified encryption functions. Most operate by grabbing a block of data at a time and frequently using a simple scrambling algorithm to modify the bits. If this scrambling is done repeatedly, then there is no known practical way to forecast the outcome. It is not, in common, practical for someone to alter the original data in any way while ensuring that the similar output will emerge from the hash function. These hash-based signature algorithms use a cryptographically secure hash function, such as Message Digest 5 (MD-5) or Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA), to make a hash value from a given piece of data.
Because the digital signature procedure is essential to the idea of a digital certificate (and in turn, the digital certificate is the primary tool to ensure e-commerce security), it's valuable to look at a diagram of the process. Figure 2.1 illustrates the steps taken by a sender informing a digitally signed message; in addition to the steps a recipient takes in verifying that the signed message is legal.
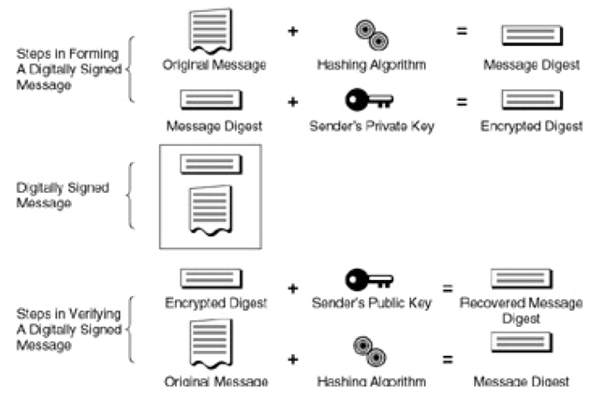
Figure: Steps in forming and verifying a digitally signed message
The primary step is to take the original message and work out a "digest" of the outgoing message via a hashing algorithm. The effect is a "message digest," which is usually depicted as a long string of hexadecimal digits (and manipulated by software as binary data). In the next step, the sender uses his private key to encrypt the message digest.
The original message content, jointly with the encrypted digest, makes a digitally signed message, as depicted in the center of Figure 2.1. This digitally signed message is appropriate for delivery to the receiver. On receipt, the recipient checks the digital signature using an opposite set of steps: first, the encrypted digest is decrypted using the sender's public key. After that, this result is compared to an independent calculation of the message digest value using the hashing algorithm. If the two values are the identical, the message has been effectively verified.
No real encryption of the message content itself require take place. Only the digital signature itself is encrypted while the message is in transfer (if not, of course, there are privacy issues, in which case the message content should be encrypted as well).
Why is a digital signature compelling verification that only the proposed signer could have created the message? For instance, what if interlopers were to change the original message? It was not encrypted, nevertheless, and could have been altered by a third party in transit. The answer is that if such a alter had been made, then the decrypted, original message digest wouldn't have matched the recomputed one for the changed data in the
Message. Confirmation of the digital signature would be unsuccessful. Likewise, the formation of a bogus signature is not practical because an interloper doesn't have the suitable private key.