Given that x=2 is a zero of P ( x ) = x3 + 2x2 - 5x - 6 determine the other two zeroes.
Solution
Firstly, notice that we actually can say the other two since we know that it is a third degree polynomial and thus by The Fundamental Theorem of Algebra we will contain exactly 3 zeroes, with some repeats possible.
Thus, since we know that can write P (x) as, x=2 is a zero of P ( x ) = x3 + 2 x2 - 5x - 6 the Fact 1 tells us that we
P (x) =(x - 2) Q (x)
and Q ( x ) will be a quadratic polynomial. Then we can determine the zeroes of Q (x) by any of the methods which we've looked at to this point & by Fact 2 we know that the two zeroes we obtain from Q ( x ) will also by zeroes of P ( x ) . At this point we'll contain 3 zeroes and thus we will be done.
Hence, let's find Q (x) . To do this all we have to do is a quick synthetic division as follows.
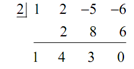
Before writing down Q ( x ) remember that the final number in the third row is the remainder and that we know that P ( 2) have to be equal to this number. Thus, in this case we have that P ( 2) = 0 . If you think regarding it, we have to already know this to be true. We were given into the problem statement the fact that x= 2 is a zero of P (x) and that means that we ought to have P ( 2) = 0 .
Thus, why go on regarding this? It is a great check of our synthetic division. As we know that x= 2 is a zero of P ( x ) and we obtain any other number than zero in that last entry we will know that we've done something incorrect and we can go back and determine the mistake.
Now, let's get back to the problem. From the synthetic division,
P (x) =(x - 2) ( x2 + 4 x + 3)
Thus, this means that,
Q (x) = x2 + + 4 x + 3
and we can determine the zeroes of this. Here they are,
Q ( x )= x2 + 4 x + 3 = ( x + 3) ( x + 1)
⇒ x= -3, x = -1
Thus, the three zeroes of P ( x ) are x= -3 , x= -1 & x=2 .
As an aside to the earlier example notice that now we can also completely factor the polynomial get,
P ( x ) = x3 + 2 x - 5x - 6 .
Substituting the factored form of Q ( x ) into P ( x ) we
P (x ) = ( x - 2) ( x + 3) (x + 1)