Q. Determine the time delay of the cable?
An RG-213/U (radio guide 213/universal coaxial cable) is a small-sized, flexible, double-braided cable with silvered-copper conductors, and a characteristic impedance of 50 �. The characteristic impedance ¯Z0(= R0) is related to the cable's geometrical parameters by
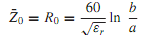
where εr is the relative permittivity (dielectric constant) of the dielectric, and b and a are the radii of the outer and inner conductors, respectively. The velocity of wave propagation in a coaxial line is vg = c/√εr , where c = 3 × 108 m/s is the velocity of light. The cutoff frequency, given by
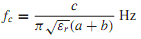
puts an upper bound for wave propagation. The attenuation due to conductor losses is approximately given by
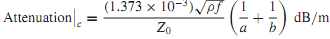
where ρ is the resistivity of the conductors. Attenuation due to dielectric losses is given by
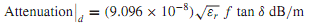
where tan is known as the loss tangent of the dielectric.
wth a = 0.445 mm, b = 1.473 mm, εr = 2.26 for polyethylene dielectric, tan δ = 2×10-4, and ρ = 1.63×10-8�m, calculate the total line attenuation at 100 MHz, and check the value of ¯Z0(= R0) in the specification. If the cable connects an antenna to a receiver 30 m away, determine the time delay of the cable, the velocity of wave propagation, and the cutoff frequency.