Determine the shear stress in each section - cells:
In Figure, the mean dimensions of the two cells are 100 mm × 50 mm and 50 mm square.
t1 = 3 mm, t2 = 6 mm, t3 = 3 mm
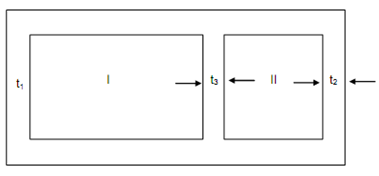
Figure
Determine the shear stress in each section, and the angle of twist per metre length for a torque of 3000 Nm. G = 80,000 N/mm2.
Solution
A1 = (100 × 50) = 5000 mm2
A2 = 50 × 50 = 2500 mm2
Z1 = (2 × 100) + 50 = 250 mm
Z 2 = (2 × 50) + 50 = 150 mm
Z3 = 50 mm
τ1 t1 = τ2 t2 + τ3 t3
⇒ τ1 × 3 = τ2 × 6 + τ3 × 3
3 τ1 = 6 τ2 + 3 τ3 ---------- (1)
T = 2 (τ1 t1 A1 + τ2 t2 A2 )
⇒ 3000 × 103 = 2 [τ1 × 3 × 3000 + τ2 × 6 × 2500]
⇒ τ1 + τ2 = 50 -------- (2)
(τ1 Z1 + τ3 Z3 ) / A1 = (τ2 Z2 - τ3 Z3 )/A2
(τ1 × 250 + τ3 × 50) /5000= (τ2 × 150 - τ3 × 50)/ 2500
⇒ 5 τ1 + τ3 = 6 τ2 - 2 τ3
⇒ 5 τ1 = 6 τ2 - 3 τ3 ------------ (3)
(3) - (1) ⇒ 2 τ1 = - 6 τ3
τ1 = - 3 τ3 ---------- (4)
From (1),
3 (- 3τ3 ) = 6 τ2 + 3 τ3
τ2 = - 2 τ3
From (2),
- 3 τ3 - 2 τ3 = 50 --------- (5)
τ3 = - 10 N/mm2
τ1 = - 3 (- 10) = 30 N/mm2
τ2 = - 2 (- 10) = 20 N/mm2
∴ θ= (τ1 Z1 + τ3 Z3 ) l /2G A1 , Here l = 1000 mm
= [30 × 250 + (- 10) × 50]/ (2 × 80 × 103 × 5000) × 1000
= 8.75 × 10- 3 radians