Determine the normal stresses:
A short hollow pier 1.6 m × 1.6 m outsides as well as 1.0 m × 1.0 m intersides supports a vertical load of 2000 kN at a point located on a diagonal 0.5 m from the vertical axis of the pier. Determine the normal stresses at the 4 corners of the section of the pier, neglecting its self weight.
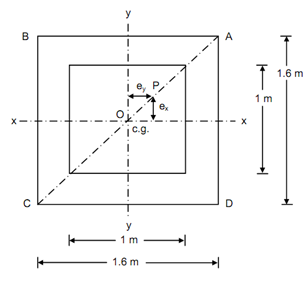
Figure
Solution
Figure illustrated the section of the pier. At point P, the load of 2000 kN is applied on the pier.
Area of cross-section A = 1.62 - 1.02 = 1.56 m2.
Section modulus, Z xx= Z yy 1.60 - 1.00 × (2/60) = 0.5875 m3
Eccentricity about XX-axis = Eccentricity around YY-axis
= 0.50 sin 45o = 0.353 m
Bending moment around XX-axis = Bending moment around YY-axis
= (2000 × 0.353)
= 706 kNm
Direct stress, f0 = P/ A =2000/1.56 = 1282.05 kN/m2 (compressive)
Bending stress around XX-axis = Bending stress around YY-axis
=± M/ Z =± 706 / 0.5785 = ± 1220.4 kN/m2
∴ Resultant stresses at corners,
f = (P/ A) ± M xx/ Z xx ± M yy/ Z yy
Stress at corner A = 1282.05 + 1220.4 + 1220.4
= 3722.85 kN/m2 (compressive)
Stress at corner B = 1282.05 - 1220.4 + 1220.4
= 1282.05 kN/m2 (compressive)
Stress at corner C = 1282.05 - 1220.4 - 1220.4
= - 1158.75 kN/m2 (tensile)
Stress at corner D = 1282.05 + 1220.4 - 1220.4
= 1282.05 kN/m2 (compressive)