Determine the example of Rate of return of a Bond
A bond is paying 10 % interest per annum and is going to mature in next two years At maturity it would pay its principal amount of 100$. If expected return on bonds today are (i) 7 %, (ii) 10 % and (iii) 15 %, what value would you pay for the bond today.
Solution
By using the above formula for situation 2, we can say that
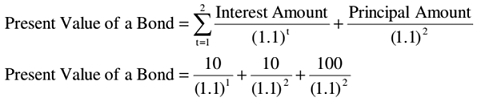
Or to use the tables the change would be:
Present Value = 10 * (PV AF2, 0.1) + 100 * (PVIF2, 0.1)
Substituting the values we find that
Present Value = 100
This is no magic. When you are getting a 10 % return and expect a 10 % return, price you would pay would equal the par value of bond. This means that if we expect higher return i.e. 15% in situation (iii) above, price which we would be willing to pay for a bond returning only 10 % would be less than par value. In the same way, if we expect lower return, i.e., 7% in situation (i) above, price that we would be willing to pay for a bond returning 10 % would be higher than par value. Can you find out the values for these two cases?
There are five variables in this case: (1) present value (2) future value (3) interest amount paid (4) return expected and (5) time period. Properties of mathematics say that if any four of these five variables are given, you can always find value of fifth variable. You can attempt that yourself or turn over to solve illustrations to look at a similar case.