DETERMINATION OF FIXED EXCHANGE RATE:
In the flexible exchange rate regime, exchange rates are highly volatile which leads to uncertainties in the international payments/transactions. For most developing countries, such uncertainties are unacceptable especially considering their development agenda.
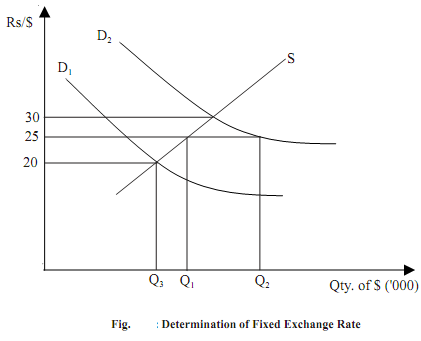
Therefore, stability in exchange rate is maintained through government intervention. Let us consider a simplified analysis of how a fixed exchange rate system operates. As given in Fig. 18.1, S is the supply curve and D1 and D2 are the demand curves for foreign exchange (say, dollar). The equilibrium exchange rate with respect to S and D2 is Rs.30/$. Assume that the government intervenes to ensure that the exchange rate is maintained at Rs. 25/$. When exchange rate is Rs.25/$ demand for dollar is higher than supply of dollar. In order to ensure that the exchange rate does not rise to Rs. 30 per dollar (which is required by supply-demand equilibrium), the government needs to sell Q1 Q2 dollars. On the other hand, suppose prevailing demand conditions are depicted by the demand curve D1 , where equilibrium exchange rate dictated by supply-demand condition is Rs.20/$. In this case, the government needs to buy Q1Q3 dollars from the foreign exchange market to ensure that the exchange rate is maintained at Rs. 25/$.
The buying/selling of the foreign exchange to maintain a given exchange rate implies that the government maintains foreign exchange reserves. (By definition, foreign exchange reserves include foreign currencies, gold reserves and SDRs). For example, BoP deficit (i.e., the demand for foreign currency (imports) is higher than the supply of foreign currency (exports)), is adjusted against the foreign exchange reserves maintained by the country. As such, the monetary authorities will suffer a loss of reserves. Similarly, a BoP surplus implies that there is a rise in the country's foreign exchange reserves. Recall from previous unit that in a flexible exchange rate regime, BoP surplus/deficit results in exchange rate appreciation/depreciation.
At any given point in time the foreign exchange reserves of a country are limited. Therefore, continuous disequilibrium between demand for and supply of foreign exchange cannot be sustained. In such situations, currency is devalued (in the case of deficit) and revalued (in the case of surplus). When devaluation takes place, exports become cheaper (i.e., rise in supply of foreign currency) and imports become expensive thereby initiating a balance between demand and supply forces.