Describe the various types of RNA?
Types of RNA : There are three different types of RNA, all formed by transcription from DNA:
(1) Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single uncoiled strand that contains information transferred from DNA and is used to direct protein synthesis. Each strand of mRNA is a template for assembly of a single polypeptide and is formed from a segment of DNA called a gene. Large protein molecules are generally formed from more than one polypeptide chain, so the information is contained on more than one gene. If a gene is not actively engaged in forming mRNA, it is said to be inactive, or turned off.
Messenger RNA is very rapidly degraded in the cell. The half-life, or the time required for degradation of half of the molecules in bacterial cells, is measured in minutes, but in eukaryotic cells the half-life is hours or even days. This is relatively short compared to the long life of rRNA and tRNA.
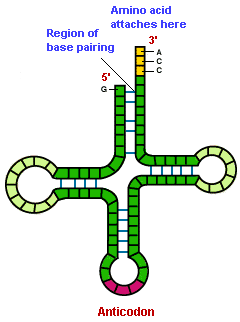
(2) Transfer RNA (tRNA) consists of 20 types of small molecules, each with about 75-80 nucleotides. Some of these nucleotides are folded together with hydrogen bonds between adjoining base pairs to give the molecule its characteristic configuration. At one end is an attachment site for amino acids; each amino acid binds with a particular type of tRNA. At the other end of the tRNA molecule is a site, called an anticodon, that binds with mRNA.
Each of the 20 tRNA species has its own code that allows complementary base pairing with a specific code on the mRNA strand. Molecules of tRNA are present in multiple copies, since they are used as tools rather than translated directly into protein.
(3) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a globular form and is the major constituent of ribosomes, membrane-bound organelles where protein synthesis takes place. Cytoplasmic ribosomal RNA from eukaryotic cells is usually composed of four subunits defined by their sedimentation coefficients, or S values, a quantity related to rate of sedimentation in a sugar solution. The smallest sphere is a single rRNA molecule with a sedimentation coefficient of 18S. The larger subunit contains three molecules of RNA--one with a sedimentation coefficient of 28S, the other two 5S and about 5.8S.