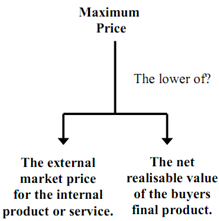
Q. Describe the Maximum transfer price?
Normally the maximum transfer price a buyer would pay would be the market price it could obtain the raw material, component, service, product etc. from elsewhere. Rational economics would indicate there is no point paying any more than you have to, especially if you are running a profit centre. The external market price is therefore generally the opportunity cost and therefore maximum transfer price a buyer is normally prepared to pay.
In certain extreme and rare cases the actual net revenue (selling price the buyer ultimate sells the product for less their own variable (marginal) cost), could be less than the external market price for the buyer, in which case the buyer would be willing to pay less than the external market price, or face making a loss when ultimately selling the product.
For example a buyer could buy a component from an alternative external supplier for £65; it sells this after its own further processing cost of £20, for only £75. In this case maximum transfer price a buyer could pay would be just £55, £10 less than actual external market price. This is because the buyer can just about break-even at a £55 maximum transfer price (selling price ultimately £75, less buyers further cost £20, less maximum transfer price £55 = nil profit), the buyer in this case would be indifferent at a maximum transfer price of £55. The £55 in this case similar to the principle of net realisable value for the buyer's product. It is worth noting that at £65 external market price the buyer's product would be uneconomical to sell.
Mathematically the opportunity cost approach will set a maximum and minimum pricing range for a buyer and seller respectively. So long as a range exists e.g. the buyer's maximum price is greater than the sellers' minimum price, then supply will take place and it would be in the group's best interest for supply to take place. The actual transfer price should be set within the range calculated, to ensure both seller and buyer are motivated to trade, the price eventually found by politics and compromise between the two internal managers, so long as the transfer price is negotiated in between the pricing range then both seller and buyer will be motivated to trade.
If opportunity cost approach doesn't produce a pricing range e.g. the maximum price is less than the minimum price, no range exists, and therefore no transfer price can be agreed so whatever transfer price is set either the seller or the buyer (or both) will not be motivated to trade. Mathematically the opportunity cost approach will ensure goal congruence, in relevant costing terms, if an internal seller cannot produce a product any cheaper than what an external group supplier would charge, then internal supply should not take place therefore the buyer will operate in the best interests of the group as a whole.