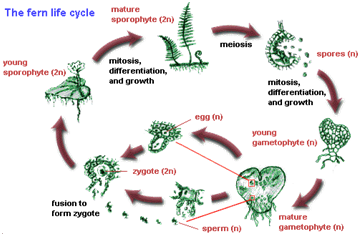
Describe Alternation of Generations?
Alternation of Generations : In meiosis, four haploid daughter cells are formed from one diploid mother cell. The life cycles of sexually reproducing organissm are divided into two phases, a haploid 1N phase, and a diploid 2N phase.
In simple organisms such as fungi, the haploid phase, which follows meiosis, extends through most of the life cycle. Eventually, one of the haploid cells becomes specialized to form a gamete, or sex cell. Gametes fuse, and the resulting diploid cell undergoes meiosis to form another haploid generation. In this case, the diploid phase is very short.
In mosses and ferns, haploid and diploid phases alternate so that there are two distinct forms, or generations, of the plant. One form is haploid and the other is diploid. In mosses, the haploid phase is most prominent, and in ferns, the diploid stage forms the large frond which we recognize as a fern. This type of organism, which alternates between haploid and diploid, is said to undergo alternation of generations in the life cycle.