Q. Describe about Dioxides?
These are generally obtained by heating the element in air. The dioxides of Se and Te can also be prepared by treating the element with conc. HNO, followed by heating the oxoacid formed e.g.
Se+ 4HNO3------------> H2SeO3+ 4NO2 + H2O
H2SeO3---------------> SeO2 + H2O
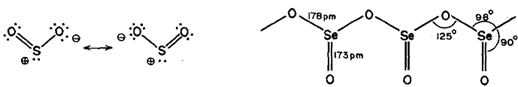
SO2, is a gas, SeO2, is a white volatile solid while TeO2, is a non-volatile white solid. Gaseous SO2, and SeO2, have discrete symmetrical molecules which are bent or angular: Fig. (a). On solidification SeO2, forms long polymeric chains, Fig.(b).
So2 and SeO2 are acidic oxides as they form acids when dissolved in water whereas TeO2 is slightly soluble in water and is an amphoteric oxide.
SO2+ H2O ---------------> H2SO3 (sulphurous acid)
SeO2 + H2O-------------> H2SeO3 (selenous acid)
SO2 combines reversibly with oxygen in the presence of platinised asbestos or vanadium pentoxide to give sulphur trioxide. This reaction forms the basis of the Contact Process for manufacturing sulphuric acid as you will study later.

Volatile sulphur compounds mainly SO2 are released into atmosphere as a result of combustion of sulphur containing fossil fuels. SO2 released in densely populated area does great damage to the respiratory organs of human beings and animals to buildings and perhaps most seriously to plants and aquatic life as a result of acid rain.
SO2 is a strong reducing agent in aqueous solution. The following reactions show this
2FeCl3+SO2 + 2H2O-------------> 2FeCl2+ H2So4+ 2HCl
Cl2+SO2 + 2H2O--------------> 2HCl + H2SO4
2KMnO4 + 2H2O + 5SO2--------> K2So4 + 2MnSO4 + 2HeSo4
Presumably the bleaching effect of SO2 also depends upon its reducing properties.
SO2 oxidises hydrogen sulphide to s provided moisture is present. At 1273 K it oxidises carbon to carbon dioxide.
2So2 + H2S-----------------> H2So4+ 3S
So2+C-------------------------> CO2+ S