DEPTH FIRST SEARCH (DFS)
The approach adopted into depth first search is to search deeper whenever possible. This algorithm frequently searches deeper through visiting unvisited vertices and whenever an unvisited vertex is not determined, it backtracks to earlier vertex to find out whether there are yet unvisited vertices.
As seen, the search described above is inherently recursive. We can determine a very simple recursive process to visit the vertices within a depth first search. The DFS is more or less alike to pre-order tree traversal. The procedure can be described as below:
Begun from any vertex (source) in the graph and mark it visited. Determine vertex that is adjacent to the source and not earlier visited via adjacency matrix & mark it visited. Repeat this procedure for all vertices that is not visited, if vertex is determined visited in this procedure, then return to the earlier step and begin the same process from there.
If returning back toward source is not possible, then DFS from the originally chosen source is complete and begin DFS using any unvisited vertex.
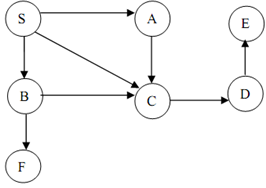
Figure: A Digraph
Let the digraph of Figure. Begun with S and mark it visited. Then visit the next vertex A, after that C & then D and finally E. Now there are no adjacent vertices of E to be visited next. Thus, now, backtrack to earlier vertex D as it also has no unvisited vertex. Now backtrack to C, then A, finally to S. Now S has an unvisited vertex B.
Begun DFS with B as a root node and then visit F. Now all of the nodes of the graph are visited.
Figure shows a DFS tree with a sequence of visits. The first number mention the time at which the vertex is visited first and the second number mention the time upon which the vertex is visited throughout back tracking.
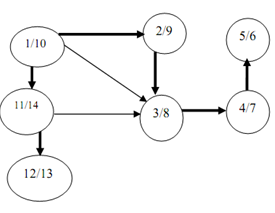
Figure: DFS tree of digraph of above figure
The DFS forest is illustrated with shaded arrow in above Figure.