Q. Definition of Random Variables?
Ans.
Up to this point, we have been looking at probabilities of different events. Basically, random variables assign numbers to elements in a sample space. Random variables are understood best if we first look at a few examples and then define the term afterwards.
If a coin is tossed four times, then we can define a random variable X to be the number of heads tossed, so X can be an integer between 0 and 4.
We can define a random variable to be the number of phone calls a company receives in one day. It can take on integer values between 0 and some very large number.
Random variables can take on values other than integers; for example, let X be a random variable representing a person's height.
Definition
A random variable is a variable that assumes a unique numerical value for each of the outcomes in the sample space of a probability experiment.
We normally denote random variables with capital letters (X, Y, etc.) and denote the actual numbers taken by random variables with small letters (x, y, etc.). So if X is the number of cars in the parking lot, then P(X = x) is the probability that there are x cars in the parking lot.
Random variables can be classified into two types:
Discrete random variables take on integer values.
Continuous random variables take values in some interval of real numbers.
Let f(x) = P(X = x). Then f(x) is called the probability function of X. f(x) assigns probabilities to the values of the random variables.
All probability functions have two properties:
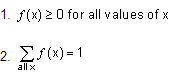
Notice that these properties ensure that for all f(x) ≤ 1 for all x.