Definition 1: Given the function f (x ) then
1. f ( x ) is concave up in an interval I if all tangents to the curve on I are below the graph of f ( x ) .
2. f ( x ) is concave down in an interval I if all tangents to the curve on I are above the graph of f ( x ) .
To illustrated that the graphs above do actually have concavity claimed above here is the graph again (blown up a little to make things clearer).
Thus, as you can illustrates, in the two upper graphs all tangent lines sketched in are all below the graph of the function so these are concave up. In the lower two graphs each tangent lines are above the graph of the function so these are concave down.
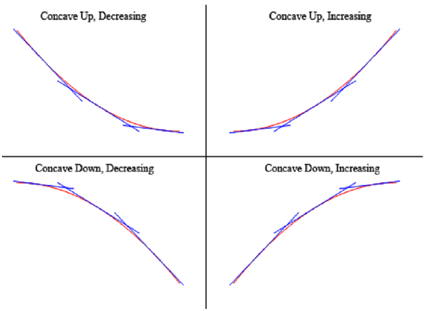
Again, notice as well that concavity & the increasing/decreasing aspect of the function is totally separate and do not contain anything to do with the other. It is important to note since students frequently mix these two up and utilizes information regarding one to get information regarding the other.
There's one more definition which we need to get out of the way.
Definition 2 : A point x = c is called as an inflection point if the function is continuous at particulate point and the concavity of the graph changes at that specified point.
Now that we contain all the concavity definitions out of the way we have to bring the second derivative into the mix. We did after all beginning of this section saying we were going to be utilizing the second derivative to obtain information regarding the graph. The given fact relates the second derivative of function to its concavity.
Fact: Given the function f ( x ) then,
1. If f ′′ ( x ) > 0 for all x within some interval I then f ( x ) is concave up on I.
2. If f ′′ ( x ) < 0 for all x within some interval I then f ( x ) is concave down on I.
Notice as well that this fact tells us that a list of probable inflection points will be those points where the second derivative is zero or doesn't present. However, be careful to not make the supposition that just because the second derivative is zero or doesn't exist which the point will be an inflection point. We will just know that it is an inflection point once we find out the concavity on both of the sides of it. Only it will be an inflection point if the concavity is different on both of the sides of the point.