Define the Wave Nature of Sound
Sound is called a longitudinal wave because the vibrations are in the same direction as the motion and speed of the wave. This is most easily pictured if you imagine a SlinkyTM stretched lightly across a tabletop. If your friend holds the far end and you pinch together a bunch of Slinky and quickly release the loops, you will see a longitudinal wave move across the Slinky. The vibration and the wave travel in the same direction, from you to your friend, across the table.
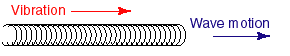
Sound is created by the alternating compression and expansion of air. Sound travels at a speed of 331 m/s in air at 0oC. The speed increases as the temperature of the air increases, at a rate of 0.6 m/s per Celsius degree. If something moves faster than sound, it is said to be supersonic. If it travels at the speed of sound, it travels at Mach 1; three times the speed of sound is called Mach 3.
The pitch of a sound is related to its frequency. A higher frequency sound has a higher pitch. Frequencies of sound waves that humans can hear range from about 20 - 20,000 hertz or cycles per second. Longitudinal waves that have higher pitch or frequency than humans can hear are called ultrasonic. Ultrasonic sound is used in sonar systems. The loudness of the sound is related to the wave's energy or intensity.
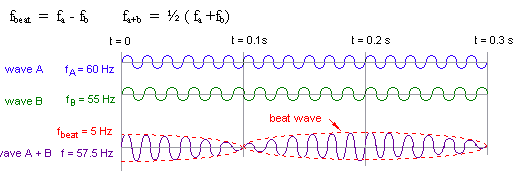
When two sound waves of slightly different frequency are added together, the resultant sound wave will have periodically changing loudness, known as the beat. The frequency of the beat is the difference in the two frequencies, and the frequency of the resultant sound is the average of the two frequencies.
Loudness and sound intensity can be confusing, because loudness is a measurement based on the sensation caused in a human by sound intensity. Because the human ear is sensitive over a very large range of intensity, loudness is defined using a logarithmic scale. (As pocket calculators have become more and more common and slide rules are used less and less, people have much less experience and comfort using logarithms.) A sound wave that is twice as loud has roughly ten times the intensity.
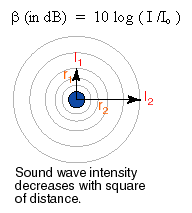
where b is the loudness measured in decibels (dB), I is the intensity of the sound wave in watt/m2 and Io is a constant equal to 1 x 10-12 watt/m2. Io represents the most faintly heard sound by humans and is defined as the loudness of 0 dB. Just as for gravity, electricity and magnetism, the intensity of sound drops off as the inverse square of the distance from the source.