Define the Critical Angle and Fiber Optics
When light is traveling in an optically dense medium, like water, and comes to the boundary of a less dense medium, like air, there are some incident angles at which the light is reflected totally internally, meaning no light is refracted into the air.
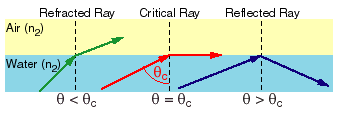
The critical angle, qc, is the incident angle at which the refracted ray is at 90o along the boundary. Snell's Law gives us the relationship between indices of refraction and critical angle:
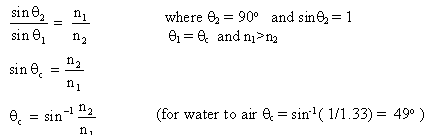
This is why when you are underwater, you cannot see anything in the air at too great an angle. Instead, you see a silvery surface at larger angles because the light is totally internally reflected. Total internal reflection allows glass prisms to reflect light more efficiently than mirrors, which have losses on the order of 3 - 10% of the light reflected. Glass prisms have an internal reflected angle greater than the critical angle for glass, which is about 42o. The diagram below shows a prism used as a retroreflector:
The fiber-optic cables that carry phone conversations and data from computer to computer also take advantage of the existence of a critical angle. If the light entering a cable is within a cone of acceptance, then it will reflect from the inside surface of the fiber-optic cable at an angle greater than the critical angle and be totally internally reflected, even if the fiber-optic cable is bent slightly. This contributes to the low losses exhibited by fiber-optic cables carrying signals.
Bundles of fiber-optic cables that are able to carry images are used in many very delicate types of surgery: such procedures are now performed using much smaller incisions, which enable a combination of camera and surgical manipulators to be introduced.