Define Recommended Dietary Allowance for Folate (RDA)?
Folate requirements are the intake levels necessary to prevent deficiency with clinical symptoms. The requirements are expressed as differences in bioavailability between dietary folate equivalents (DFE) and food folate. One DFE is equal to 1 mcg of food folate. Table 8.9 presents the ICMR and the FAO/WHO recommended nutrient intake for folic acid by groups. The individual requirement of folate for both the sexes recommended by ICMR is 100 mg/day, which increases in conditions of pregnancy and lactation to 400 and 150, respectively.
In 1998, the United States National Academy of Sciences (NAS) exhaustively reviewed the evidence regarding folate intake, status, and health for all age groups, including pregnant and lactating women. On the basis of their review, the NAS calculated estimated average requirements (EARS) and recommended dietary allowances (RDAs), taken to be the EAR plus 2 standard deviations, for folate. The 2004 FAO/ WHO Expert Consultation have adopted the RDAs of the NAS as the basis for their RNIs (Table).
Table: ICMR and FAO/WHO recommended dietary intakes for folic acid expressed as dietary folate equivalent by groups
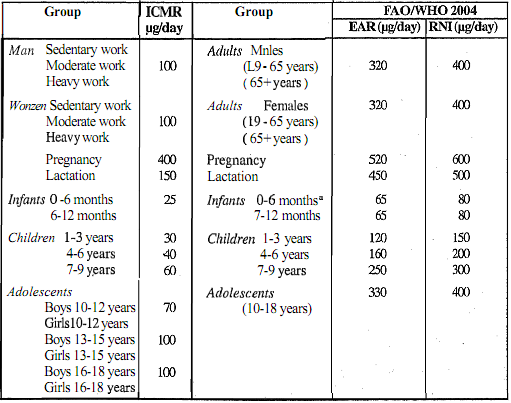
The RNIs suggested for various groups by FAO/WHO in Table assume that food folate is the sole source of dietary folate because most societies in developing countries consume folate from naturally-occurring sources. As discussed earlier, natural folates are found in a conjugated form in food, which reduces their bioavailability by perhaps as much as 5090. In addition, natural folates are much less stable. If chemically pure folk acid (pteroylmonoglutamate) is used to provide part of the RNI, by way of fortification or supplementation, the total dietary folate, which contains conjugated forms (pteroylpolyglutamates), could be reduced by an appropriate amount.