Define Protection of poly unsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) from oxidative damage?
The major biological role of vitamin E is to protect PUFAs and other components of cell membranes and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) from oxidation by free radicals. Vitamin E is located primarily within the phospholipid bilayer of cell membranes. It is particularly effective in preventing lipid peroxidation - a series of chemical reactions involving the oxidative deterioration of PUFAs. Elevated levels of lipid peroxidation products are associated with numerous diseases and clinical conditions.
Let us understand the reactions involved in the oxidative deterioration of PLFAs next. The PUFAs, you may recall studying in the Nutritional Biochemistry Course, have methylene (-CHI2-) groups located between two double bonds. This type of functionality makes PUFA particularly sensitive to the flameless oxidation in air that is called autoxidation, because the doubly allelic hydrogen atoms in these methylene carbons are very rapidly abstracted by peroxyl radicals. Free radicals are produced in normal metabolism and by the effects of toxins on tissues.
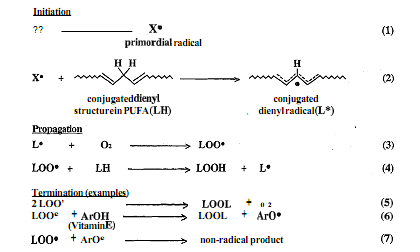
These free radicals (e.g. superoxide produced endogenously by many processes like phagocytosis) can cause the formation of lipid free radicals as shown in the initiation sequence reactions 1 and 2 in Figure. In reaction 2, initiation produces the lipid free radicals and a conjugated dienyl radical (L). The lipid radical L then undergoes the propagation sequence reaction 3 and 4 leading to the formation of lipid hydro peroxides, LOOH.
Lipid hydro peroxides produced in autoxidation processes are also formed in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. For example, the enzymes in cyclooxygenase pathway which converts arachidonic acid to several types of hydro peroxides. These have potent biological properties.
Autoxidation is a chain process. Reactions 3 and 4 continue to alternate until a termination occurs in which two radicals combine to form a new two-electron bond. When vitamin E is absent, from five to twenty five LOOH molecules are formed in reaction 4 for each primordial X radical formed in reaction 1. If vitamin E is present, it traps peroxylradicals to give stable LOOH molecule and a vitamin E radical (Ar O0 in reaction 6). The vitamin E radical is stable enough to seek another LOO* radical as in reaction 7 and complete the termination sequence. In absence of vitamin E, however, each primordial radical produces <1 molecule LOOH. Thus, vitamin E effectively stops the autoxidation chain reaction which converts PUFA to lipid hydro peroxides, LOOH. One molecule of tocopherol can effectively protect 100 or more PUFA molecules from autoxidative damage. Biological membranes generally contain - one percent as many molecules of vitamin E as molecules of PUFA.