Define Energy requirements of infants?
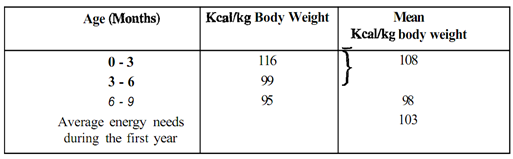
Energy: Energy requirements of infants are based on the energy intake through breast milk by infants of well-nourished mothers. Based on an average intake of breast milk/day by infants of the well-nourished mothers, ICMR (1990) has -recommended the energy allowances for infants, as given in Table.
FAO/WHO/UNU 2004 has given' the energy requirements for needs of breast-fed and formula-fed infants. Total energy expenditure (TEE) is calculated with predictive linear equation as follows:
Breast-fed:
TEE (MJ/day) = - 0.635 + 0.388 kg; n = 195, r = 0.87, see = 0.453 MJ/day (108 Kcal/day)
TEE (Kcal/day) '= - 152.0 + 92.8 kg
Formula fed
TEE (MJ/day) = - 0.122 + 0.346 kg; n = 125, r = 0.85, see = 0.463 MJ/day (110Kca/day)
TEE (Kcal/day) = - 29.0 + 82.6 kg
The energy demand for growth constitutes up to 35% of TEE at 0-3 months and 17.5% at 3-6 months. The growth requirement should be added to TEE to give total energy requirement, as you may recall studying in Unit 2 on energy requirements.
Compared with earlier recommendations (FAO/WHONNU 1985), present values are about 12% lower in first 3 months of life, 17% lower from 3-9 months and 20% lower from 9-12 months. For preschoolers (1-6 years), the energy requirements by ICMR (1990) is laid in two age categories i.e. 1-3 years and 4-6 years as shown in Table.
As per the guidelines laid by the FA01 WHO/UNU Expert Consultation (1985), the energy needs of children are computed from energy needs per kg body weight. The body weight of well-to-do children is used for this computation.
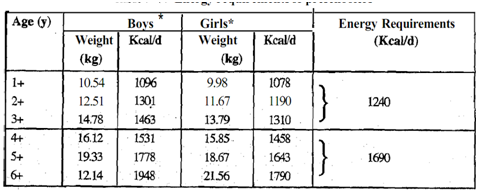
*Energy intake and weights of well-to-do children.