Define Changes in Physical Development in infants?
It seems that all infants do is to sleep and hardly Seed. In spite of this observation, a well-fed and cased infant doubles its birth weight within 4 to 6 months or life and triples within the first year, the birth weight of a normal infant should be more than 2.5 kg. Average birth weight of Indian infants ranges from 2.7-2.9 kg. A well nourished mother delivers baby weighing between 3.2-3.3 kg, which is comparable to NCHS standards.
Similarly, infants typically increase their length by 50% in the first year. At birth, their length is 50 cm which increases to 75 cm by the first year. It is imperative to monitor weight either by serially recording weight on growth charts or approximately @ 200 g/week in first three months; 150 g/week from 4-6 months; 100 g/week in 7-9 month and 50 g/week till one year.
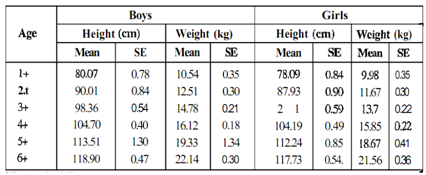
Beyond the first year, growth of the child slows down. It takes 5 years more for the weight at one year to double. The child continues to gain height but the rate is not constant. During the second year, the increase in height is 10cm and in weight is 2.0 lo 2.5 kg. During 3-6 years, the growth continues steadily. Have it look at Table. The annual gain in height is 6-7 cm and weight is 1.5-2.0 kg. Large variations are seen, as growth has no calendar and occurs in spurts.
During physical growth, the nutrient needs are high and when any nutrient is limiting at a critical phase of growth and development, the growth of the body as a whole slows down or even stops. Flattening of weight for 3-4 months indicates a danger of developing malnutrition.
Since the baby's head grows rapidly during foetal years and first year of life, by the time the child is 2 years old, the head circumference achieves nearly 2/3d of its final size. The brain grows faster around the time of the birth than at any other time of life. To accommodate this brain growth, the infant's head is larger in proportion Lo the rest of the body. After 18-24 months of age, the rest of the body eventually grows and head circumference to height ratio continues to fall.