Define Body Mass Index (BMI) or Quetelet Index?
BMI is an index measure of body fat used for the assessment of disease risk. It is a figure which gives an indication of weight for height calculated by the equation:
BMI = Weight (in kilograms) / height (in metres)2
Thus, BMI is measured in kg/m2. This index is simple, correlates to fatness, and applies to both men and women. Garrow and Webster (1985) proposed grades of obesity, as indicated in the Table.
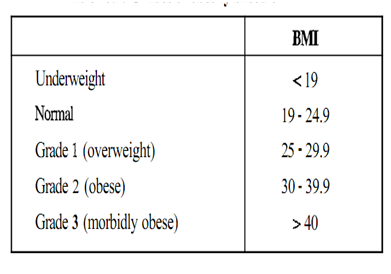
BMI only indicates the degree of being over- or underweight. It makes no account for the distribution of obesity; indeed, where fat is distributed on the body, it has been linked to an increased risk of certain diseases. BMI is more reliable for assessing disease risk (such as cardiovascular diseases) when used in conjunction with waist-hip ratio (WHR).
WHR = waist circumference (cm) / hip circumference (cm)
WHR<1 - gynoid deposition of fat (pear shaped) and reduced risk of diseases
WHR >I - android deposition of fat (apple shaped) and increased risk of diseases
BMI does not take into account skeletal size, amount of body water and, for the bodybuilder, muscle mass. Using the BMJ scale in bodybuilding puts most as 'overweight' and in many cases 'obese', even if there is very low body fat. However, it is a simple, quick method which correlates to fatness and applies to both men and women.