Define Autoclave - Food Microbiology?
For sterilization, steam under pressure is generally employed using an instrument called autoclave. Figure illustrates the autoclave. Autoclave was developed by Chamberland in 1884. As you may have noticed in Figure, autoclave is a double walled cylindrical metal vessel made of stainless steel or copper.
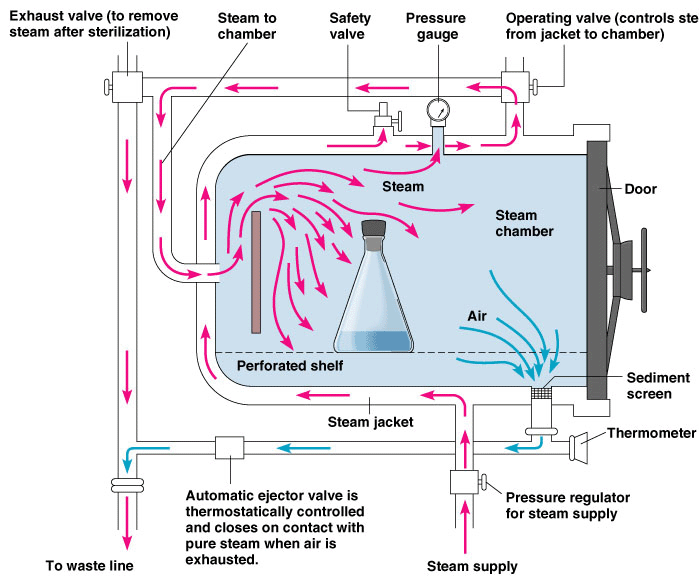
Autoclave lid is provided with the pressure gauze for monitoring the pressure, exhaust valve to remove the air and safety valve to avoid explosion during operation. The articles are kept loosely in the autoclave chamber and then water is boiled and steam is released into the autoclave's chamber. The exhaust valve is kept open till the air present in the chamber is out. The exhaust valve is then closed and pressure of the steam in the chamber is allowed to reach to the desired value. The temperature of the steam inside the chamber depends on the pressure in autoclave. Relation of autoclave pressure with the temperature of steam is presented in the Table.
Table: Relation of Autoclave pressure with the temperature of steam
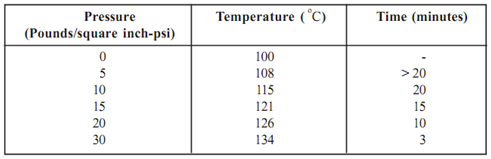
More the pressure, higher is the temperature and less is the time used for autoclaving. Generally, pressure of 15 pounds with temperature at 121° C is employed for 15-20 minutes for autoclaving.
Saturated steam heats an object about 2500 times more efficiently than dry heat at the same temperature. Steam condenses on the cooler surface of the object and transfers its heat energy to the object and sterilizes it.
Autoclave can be used for sterilizing culture media, scalpel and other heat resistance instruments, glasswares, etc. but not for oils, powders and plastics. Where autoclave is not available, pressure cooker can be used. It works on the same principle as of autoclave.